Why the fine-tuning trap hits fintech and healthcare first
In fintech and healthcare, translations have to be exact, consistent, and defensible. That’s where generic fine-tuning can be risky. It can create fluent output while mixing contexts in the background without you even noticing. You can’t afford this in regulated, high-trust industries.
In fintech, small wording changes can change meaning
Fintech content is full of terms where “close enough” isn’t good enough. Think fees, rates, risk disclosures, onboarding flows, and transaction states. If a model learns from a blended dataset you get contextual contamination in places that matter.
It might reuse phrasing that belonged to another product line or an older release, and it does it confidently. Or it can mix different markets or apply different compliance wording.
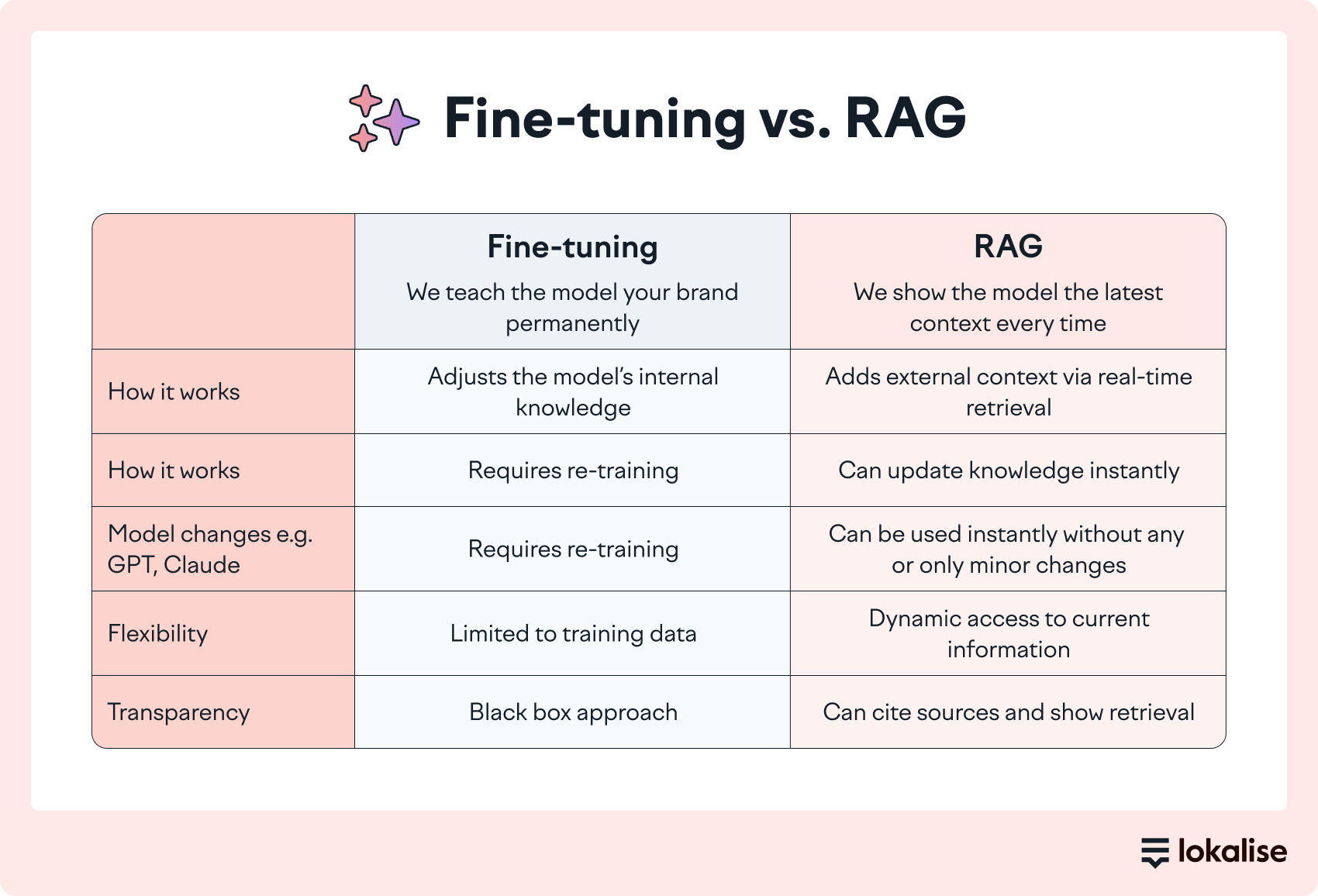
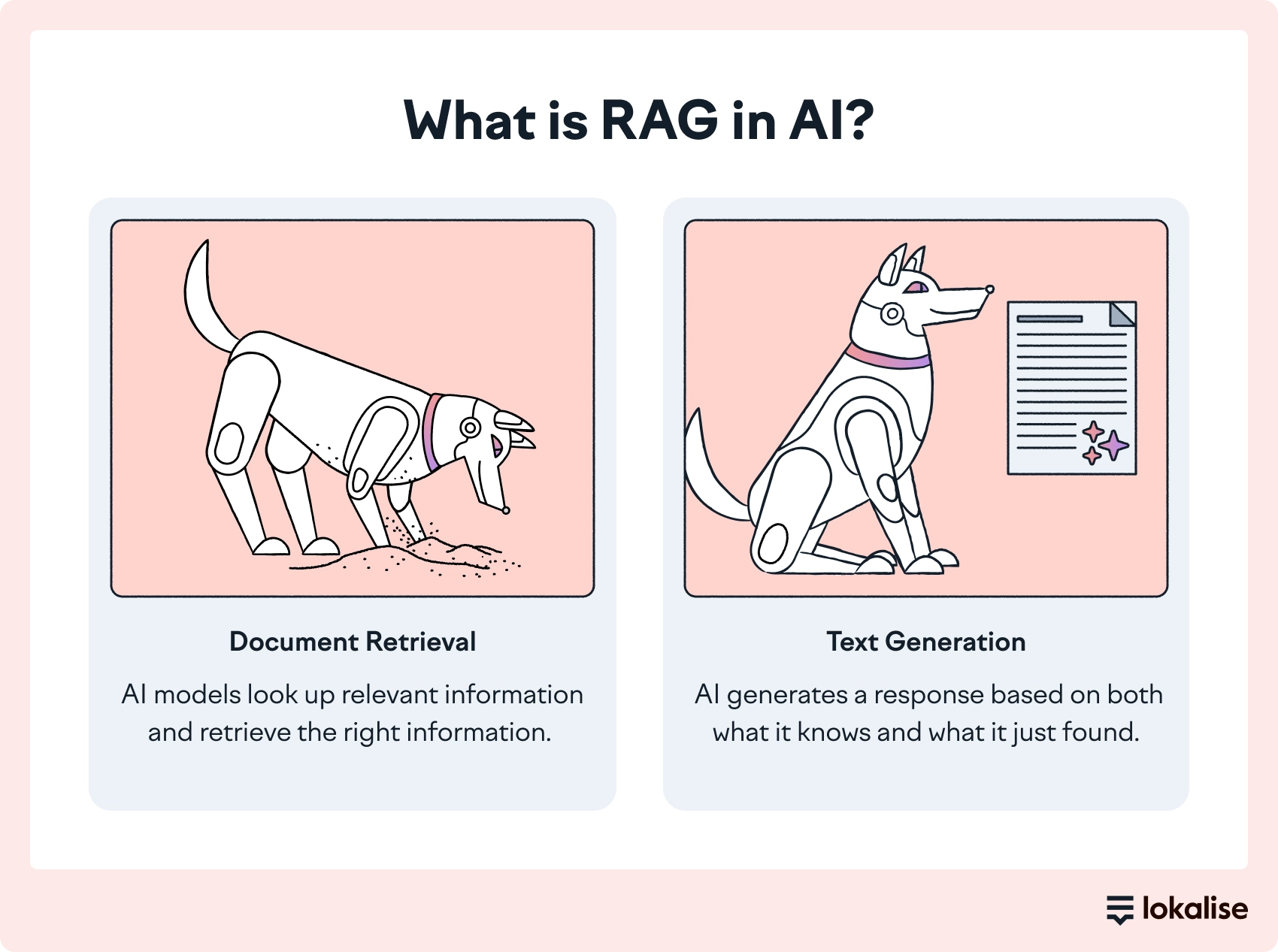
Dynamic context orchestration avoids this because the translation is grounded in what’s approved today. With RAG, the model pulls the right references at runtime. It’s the latest version of your glossary terms for financial concepts, your preferred wording from translation memory, and the style guidance for that content type.
In healthcare, “almost right” can become unsafe
Healthcare localization has the same problem, with higher stakes. Patient-facing content, instructions, warnings, contraindications, and consent language all depend on precise wording and consistency.
Generic fine-tuning can unintentionally learn inconsistent edits, outdated phrasing, or mixed clinical vs. marketing tone, and then apply those patterns where they don’t belong.
This is where RAG and domain controls matter. When the model is guided by the right references for the specific domain (approved terminology, validated phrasing, the right tone constraints) you’re relying on your current sources of truth.
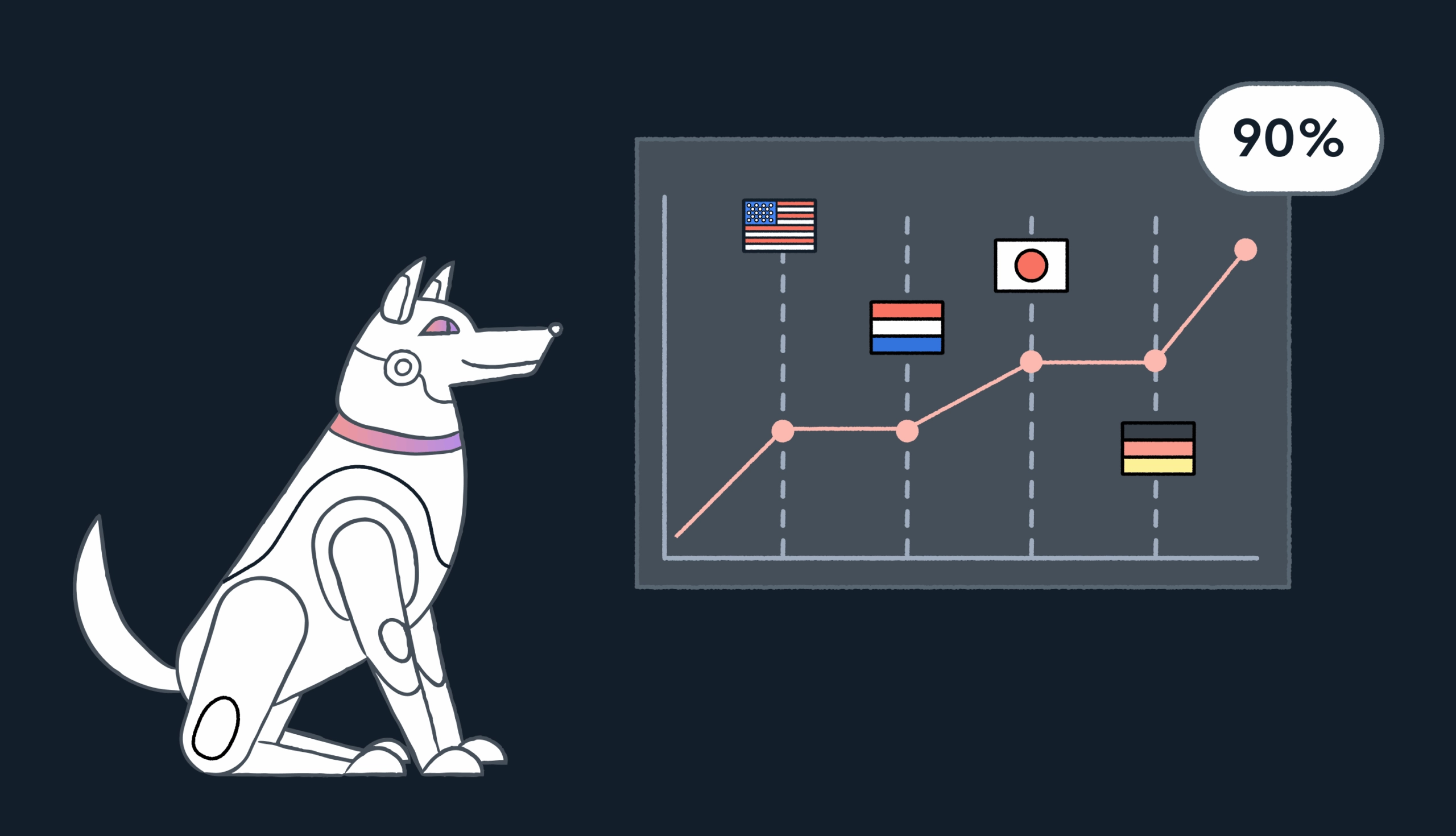
With RAG and Custom AI Profiles, AI translations can reach human-level accuracy, with around 90-95% first-pass acceptance in internal and customer evaluations.