As a Product Manager leading AI innovations at Lokalise, I’ve been closely following the latest AI news and filtering out the noise that inevitably comes with a revolutionary tech boom.
AI has moved incredibly fast since ChatGPT exploded into the mainstream in late 2022, what I like to call ‘the GPT moment’.
We’ve seen major model releases roughly every few months, from GPT-3.5 through GPT-4, GPT-4o, and most recently GPT-5 with its integrated reasoning capabilities launched in August 2025. Add to that the rapid iterations from Anthropic’s Claude series, Google’s Gemini, and other major players. The pace of change has been relentless.
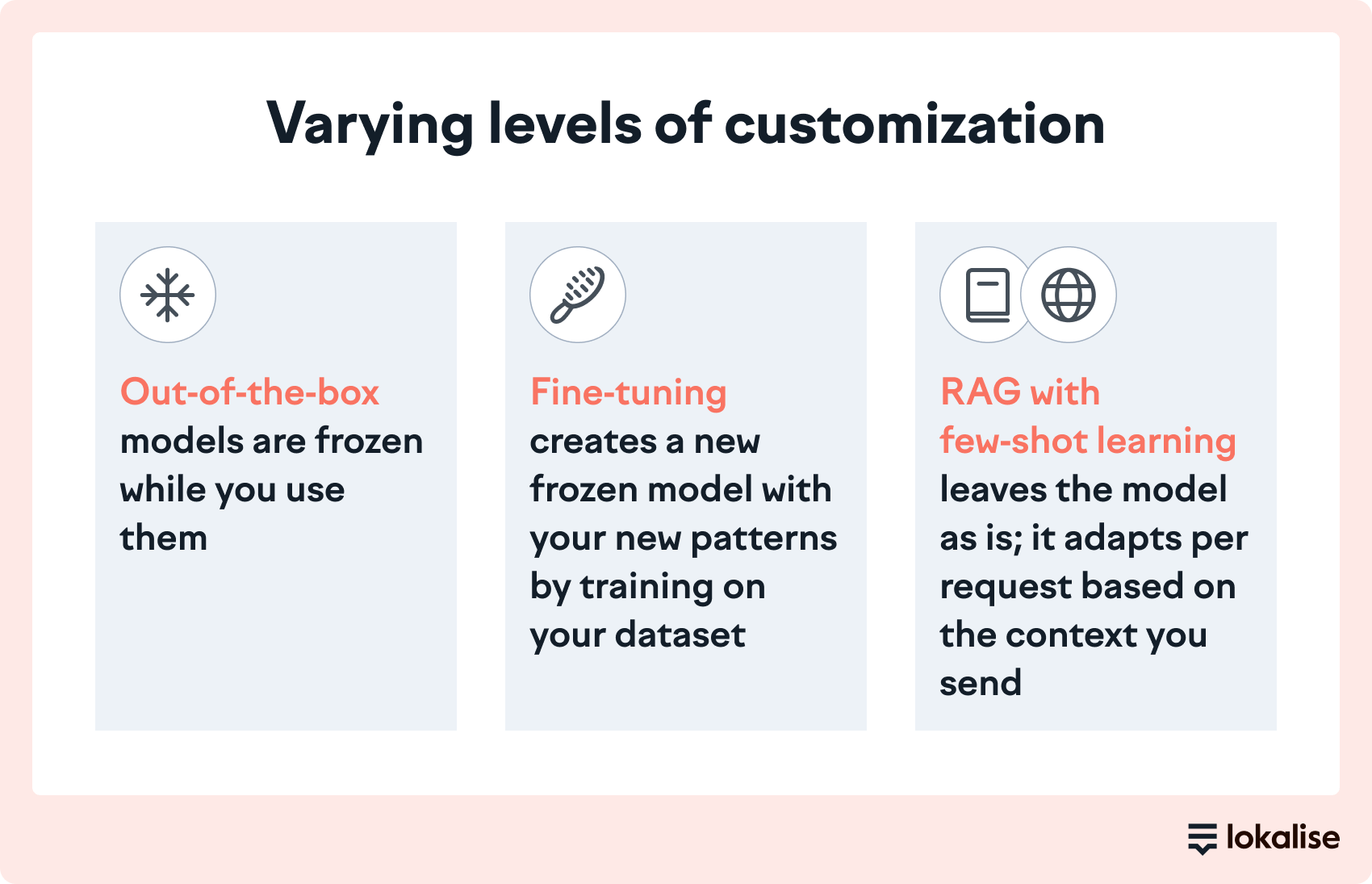
A few months ago, everyone was talking about fine-tuning, now it’s AI agents, and the conversation keeps shifting to the next big thing.
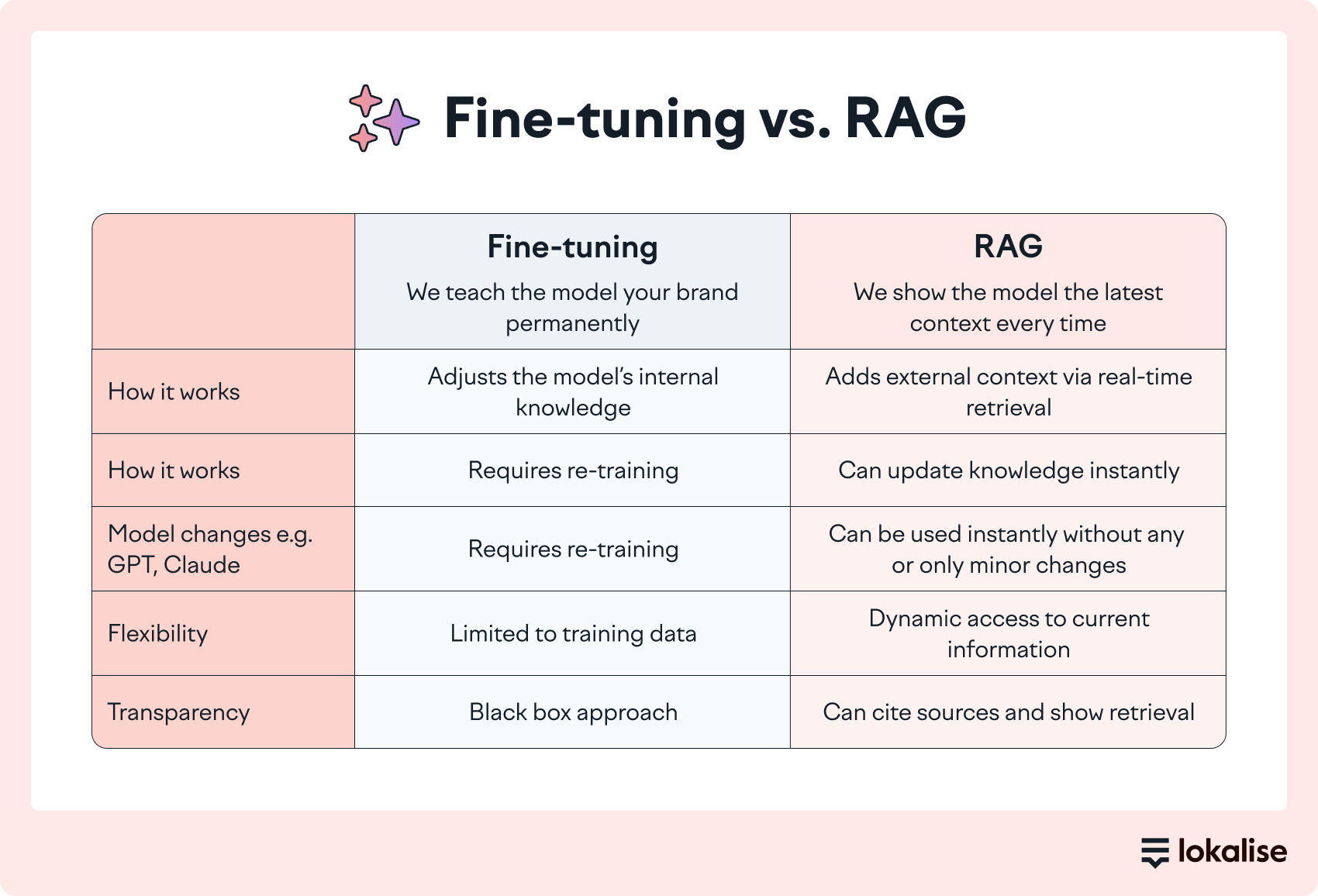
Meanwhile, I continue to talk about a framework that’s been around since 2020: Retrieval-Augmented Generation, or RAG. It was widely discussed in AI circles early on but seems to have been overshadowed by newer, flashier developments.
Despite its fleeting moment in the spotlight, RAG continues to deliver tremendous practical impact for businesses looking to make AI actually useful for real-world applications. It bridges the gap between a model that sounds smart and a system that actually knows things.
So, what is RAG?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI framework for retrieving facts. It was developed by Patrick Lewis and colleagues from the former Facebook AI Research (now Meta AI), University College London and New York University in 2020.
As the name suggests, RAG has two phases: retrieval and content generation.
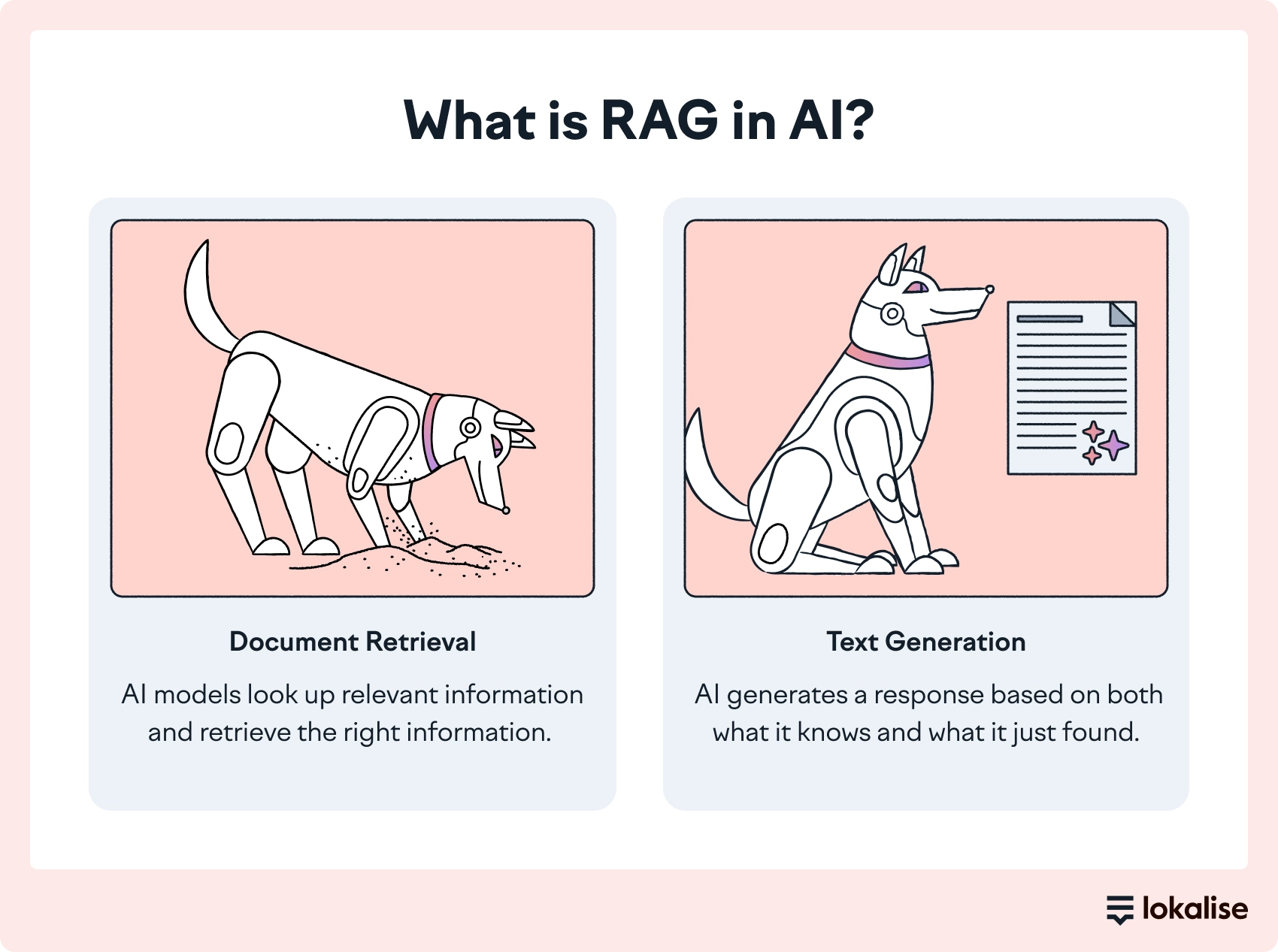
How does RAG work?
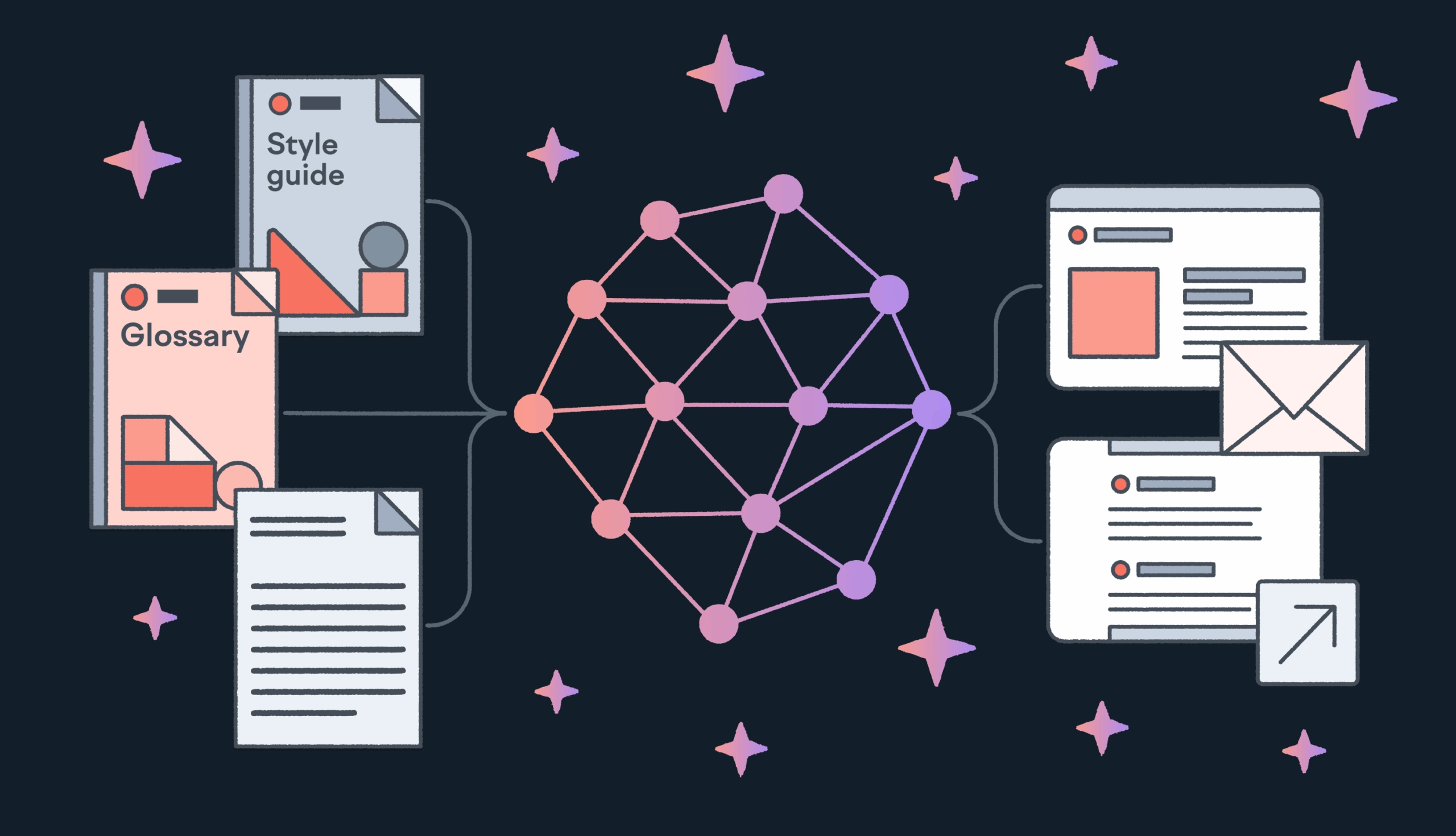
It’s like giving the AI access to a library. Instead of making AI memorize everything, the model looks up relevant information in real time from a connected knowledge base (e.g., style guide, translation history, glossary), retrieving the right information when needed, and generating a response based on both what it knows and what it just found.
Steps involved in RAG:
- Data preparation: Data sources are converted into a format systems can understand
- Query processing: Query is converted into a format the system can understand
- Retrieval: The system finds the most relevant documents that match user’s query
- Augmentation: The retrieved information is combined with the original query to create an enhanced prompt
- Generation: Large language models generate a response based on both its training data and the retrieved information
What’s key is how ‘smart’ the retrieval part is.
RAG in action: AI translation with style consistency
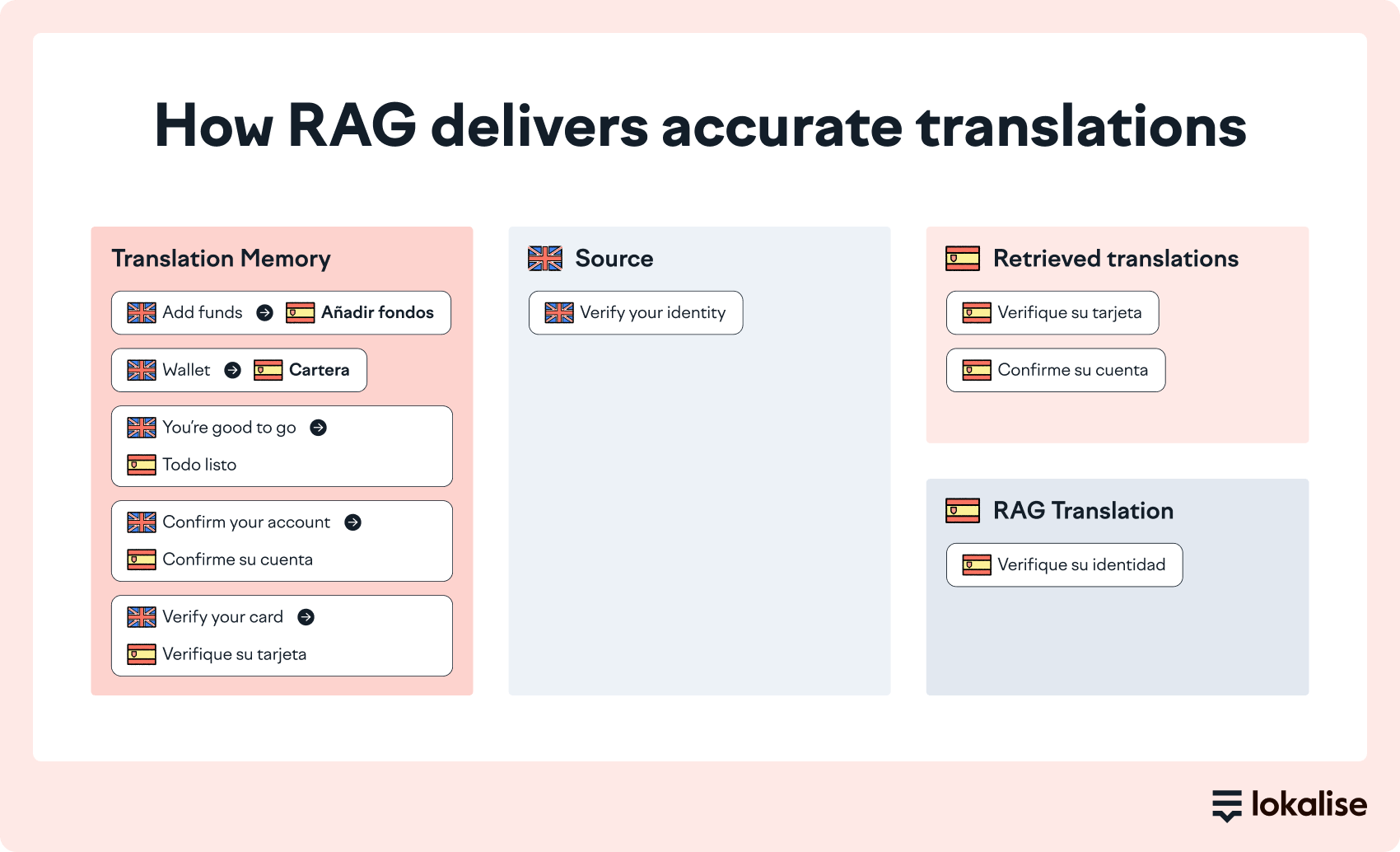
Let's say a fintech company needs to translate "Verify your identity" into Spanish for their mobile app.
Without RAG, a generic AI might produce: "Verifica tu identidad" (informal)
With RAG, the system retrieves context showing the company uses formal tone:
- Context like, previous translations (from translation memory): "su cuenta" (your account), "su tarjeta" (your card)
- Style guide: Maintain respectful, formal communication
The RAG-enhanced result: "Verifique su identidad"
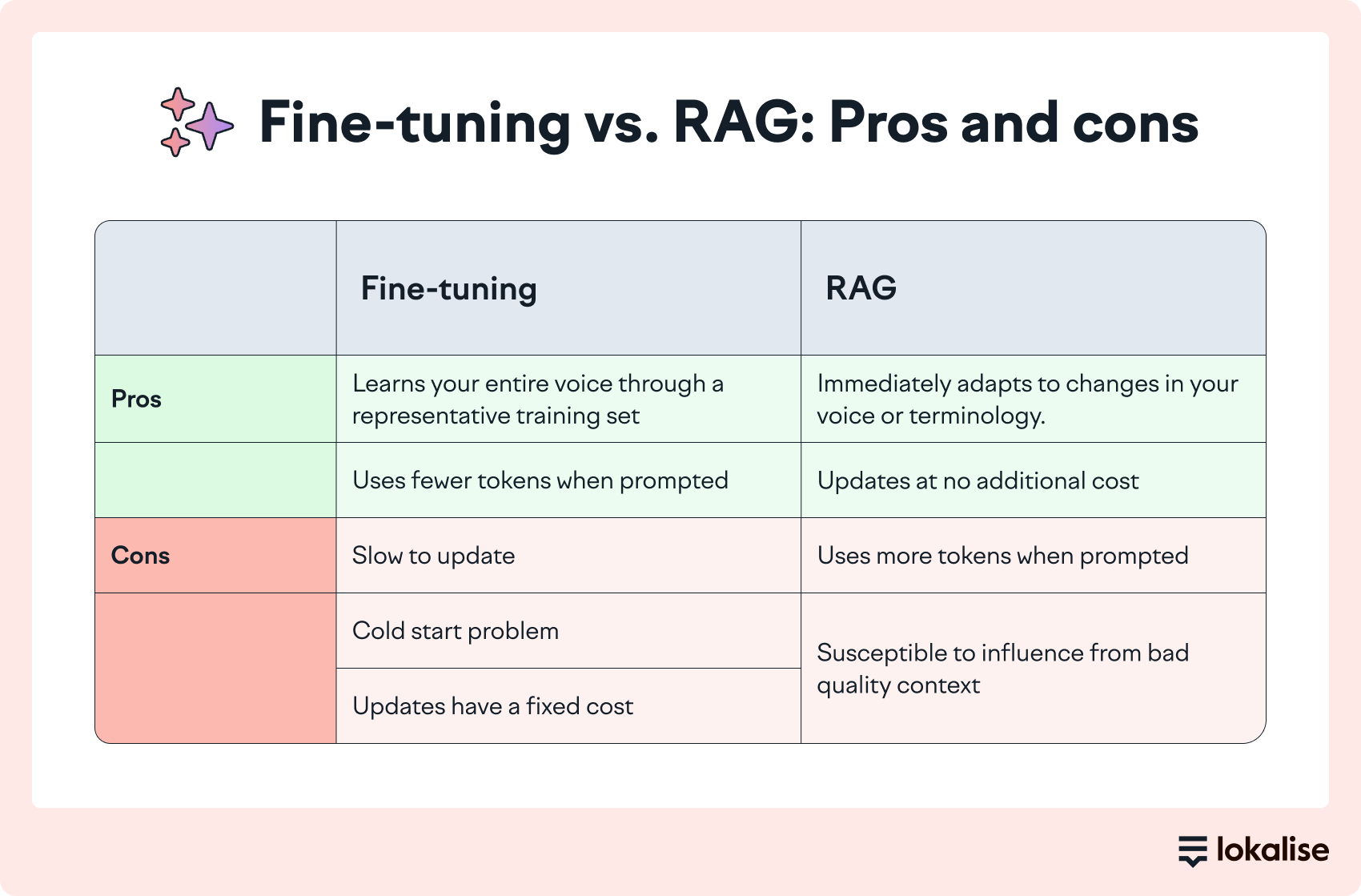
Now imagine the company rebrands to appeal to younger users and switches to informal communication.
Simply update your translation memory with informal examples ("tu cuenta", "tu tarjeta"), and RAG immediately adapts. The next translation automatically uses "Verifica tu identidad" (informal). No retraining required, just instant adaptation to your evolving brand voice, as RAG retrieves and applies the right historical examples and guidelines during generation.