When expanding globally, businesses face a strategic choice between:
- Globalization (maintaining a standardized brand across all markets)
- Internationalization (adapting your brand to local cultural preferences and customer behaviors)
Which of these approaches is best-suited to drive your growth?
In this guide, we break down the differences between globalization vs. internationalization and walk you through a decision guide to help you choose the right path forward.
Understanding the concepts: Globalization and internationalization
Globalization is the process of building more interconnected businesses, economies, and cultures worldwide by integrating economic systems. On the other hand, internationalization focuses on designing products or services that can be easily adapted to different cultures and regions.
🧠 What is localization?
Localization happens when a business adapts its products/services/content to cater to the cultural, language, and regulatory requirements of a specific market. It goes beyond basic translation and comprehensively strategizes for making your brand feel native in a particular region.
Learn more about localization to see where it fits in this puzzle.
Here’s a quick comparison of the two approaches:
| Globalization | Internationalization | |
| Cost efficiency | Higher economies of scale, lower production costs | Higher customization costs, potentially lower marketing costs |
| Market responsiveness | Limited ability to address local needs | High adaptability to local preferences |
| Operational complexity | Lower complexity with standardized processes | Higher complexity of managing different approaches |
| Brand recognition | Strong, unified global brand | Varied recognition based on local adaptation |
| Risk management | Higher vulnerability to global events | Better insulated from regional crises |
| Cultural relevance | May face cultural barriers | Higher cultural acceptance and relevance |
Globalization: Pros and cons
Let’s understand the merits and demerits of globalization before we understand which approach is better for your business.
Advantages of globalization
- Helps companies build a global customer base by streamlining cross-border operations
- Standardizes production and operational setup to create economies of scale
- Improves the standard of living across the market through economic growth
- Facilitates cultural exchange and assimilation across countries
- Allows you to deliver a cohesive brand experience globally
Disadvantages of globalization
- Increases manufacturing and shipping demands that can potentially damage the environment
- Can lead to exploitation of workers in underdeveloped regions with weaker labor protections
- Widens the economic gaps between developed and developing/underdeveloped countries
- Reduces cultural distinctiveness and local business opportunities
📚 Further reading: Learn more about globalization vs localization as well.
Internationalization: Pros and cons
Here are all the benefits and downsides of internationalization that businesses have seen so far:
Advantages of internationalization
- Creates opportunities for businesses to expand to new markets worldwide
- Encourages an innovation economy by merging different cultures
- Protects businesses against slowdowns in a single market
- Enables businesses to tap into diverse talent pools
Disadvantages of internationalization
- Requires heavy investment in market research, infrastructure, and more
- Involves complex regulations and legal frameworks across different regions
- Can dilute brand consistency and complicate quality control in multiple markets
📚 Further reading: Learn more about internationalization vs. localization as well.
Kickstart your global expansion
To help you follow in the footsteps of the 3000+ companies who’ve successfully localized, check out Global-ready growth, our guide to unlocking international revenue.
DownloadWhich is better for your business: A decision guide
Growing businesses face the difficult decision of choosing between globalization and internationalization. This choice depends on your industry, long-term vision, resources, and several other factors.
We created this decision guide outlining specific scenarios when you should pick either approach.
Pressed for time? Let’s first discuss all the key factors to consider before making up your mind about international growth.
| Factors | Globalization | Internationalization |
| Market strategy | Standardized products/services across all markets with minimal adaptation | Products/services designed from the ground up to be adaptable to different markets |
| Resources | Higher initial efficiency but potentially costly market-specific adjustments later | Higher upfront investment in flexible architecture, but smoother adaptation in every market |
| Speed to market | Faster initial global deployment with a one-size-fits-all approach | Potentially slower initial deployment, but faster expansion to new markets later |
| Cultural sensitivity | Emphasizes universal appeal and brand consistency | Emphasizes cultural adaptability and local market relevance |
| Competitive positioning | Works well for industries with universal standards/needs (like SaaS) | Works well for industries where local preferences matter significantly (e.g., food, retail) |
When to choose globalization
Now, we can break down different scenarios when globalization is a better tactic to drive business growth.
1. Your product has universal appeal with minimal customization needs
Globalization works well when your product has universal use cases without any cultural specifications.
Think about a guitar: Its strings, soundboard, and saddle remain the same, no matter which part of the world you’re in.
The key is to analyze your offering and see whether your core value proposition(s) remain constant across different markets. Do your research to understand if customers in Brazil can use your product the same way as those in Denmark.
When your products/services solve a universal problem, standardization can fuel growth. You can leverage globalization to expand worldwide.
Companies like Toyota use this approach.
Cars work the same way in every part of the world. So, Toyota sells its automobiles in over 170 countries with manufacturing facilities distributed across Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
Here’s a glimpse of Toyota’s global presence:
2. Your expansion strategy focuses on cost efficiency
Picture this: one production facility, one supply chain, and one marketing campaign catering to every country in the world.
Globalization is beneficial, especially when businesses aim to maximize every dollar. It supports market expansion and creates economies of scale, where your savings and profits increase as production grows.
Let’s understand how.
A standardized production process means you can:
- Optimize manufacturing processes
- Negotiate favorable terms with suppliers
- Spread fixed costs across higher volumes
Beyond production, you can also get better ROI on marketing expenses. It’s more cost-efficient when you can deploy the same campaign globally without the need to create localized versions.
IKEA is a good example of this approach. The brand follows a standardized approach and operational setup when setting up stores in different parts of the world. The cost efficiency allows it to pass savings to customers.
For example, the IKEA website examples how all of its stores have the same or similar layout with areas demarcated for specific purposes:
3. Your brand consistency builds customer trust
Many global brands have the same reputation in every market, like Rolex is a luxury watch brand, while Bata is a household footwear name.
The bottom line? Brand consistency reinforces your positioning in different regions. This is particularly useful to strengthen your reputation and gain customer trust, no matter where they go.
For example, when people travel from Shanghai to Stockholm, they recognize Starbucks as a well-known coffee brand. This consistency — in product/service quality, customer service, and even retail environments — can influence the overall customer experience.
You have to measure the impact of brand recognition in every market. If brand consistency builds credibility, a standardized approach will help you win.
4. Your industry operates under global standards
Some industries are global by nature. Their standards, regulations, and customer expectations align across borders.
The aviation and software sectors present good examples here. Both industries require you to follow similar protocols, security standards, and other regulations applied worldwide.
In such industries, the need for standardization creates a natural environment for globalization. When standards of operation converge at a global scale with minimal local variation, it’s best to build a standardized business model at the global scale.
When to choose internationalization
So, when does internationalization work better? Here are some use cases where internationalization becomes the key to success.
1. Your products demand significant local adaptation
Some brands have to modify (or completely redesign) their products/services to be useful for buyers in different regional markets.
The logic is simple: You can’t sell the same kind of winter coats in Siberia as you do in Sydney. If your product/service requires changes based on usage patterns, physical environments, or cultural contexts, you have to take the internationalization route.
The degree of adaptation required can vary for every industry and product category.
For example, food and beverage products require significant changes to accommodate local taste preferences and cultural variations. You might find beef burgers at McDonald’s in the United States, but not in India, where a majority of the population doesn’t consume beef.
For example, here’s the menu of McDonald’s Japan with unique items based on local preferences:
Internationalization allows brands to identify and adapt to these changes from the outset.
2. You face market-specific regulations to prevent standardization
When laws and compliance standards vary significantly across your target markets, you can’t follow a standardized setup. These regulatory differences often reflect deeper cultural values and historical contexts that your business should respect.
Here are a few ways in which regulations can hinder standardization:
- Ingredient restrictions force you to alter product formulations in different markets
- Compliance regimes in the financial, healthcare, and education sectors call for variations
- Varying privacy frameworks and data handling practices bring more differences in your policies
The biggest reason to embrace internationalization is when you can’t legally operate the same way in all target markets.
Stripe is a good example here. The payments platform has several versions of its website for different countries. Each version is customized to a market’s financial needs, currency, and more.
3. Cultural preferences directly impact your success
Your product can be perfect, but that doesn’t guarantee soaring sales across all markets.
Every region’s cultural nuances impact how people perceive and use your products/services. If your products and marketing don’t resonate with the local audience, you have to build an international expansion strategy.
Home Depot’s failure in China is a prime example of this.
Despite its success in North America, the DIY furniture brand didn’t resonate with Chinese consumers. That was largely because of a cultural divide where people didn’t want to engage in manual labor and hired professionals to build or renovate furniture.
Beyond your main offering, this factor applies to your brand positioning and marketing as well. If you follow a standardized approach and run German commercials in Indonesian markets, they’ll hardly move the needle.
4. You have to adjust to compete with local players
A globalized approach works well for companies that already have an upper hand over local competition in any market. Brands like Apple, Puma, and Nestle have established a strong global reputation where buyers in different regions associate high value with these names.
But if you’re an up-and-coming brand, you have to adapt to local conditions to win against the competition.
This is even more important when your competitors have years-long relationships with customers and finely tuned operations.
For example, when Amazon wanted to enter the Indian market, it faced stiff competition from Flipkart, a home-grown online marketplace with a solid reputation. This goes to show that not even the most dominant global brands are immune to local competition.
So, your decision to pick internationalization over globalization will come down to the kind of markets you want to target. If you’re competing against brands with home-field advantage, internationalization might be your only viable strategy.
Technical considerations for internationalization
While we’re on the subject of internationalization, let’s discuss some technical factors to consider when implementing this approach for software products:
- Text and language: Your app should support right-to-left languages like Arabic and Hebrew instead of just text direction changes. You also need UTF-8 encoding and font compatibility for handling different character sets in scripts like Chinese, Thai, and Korean.
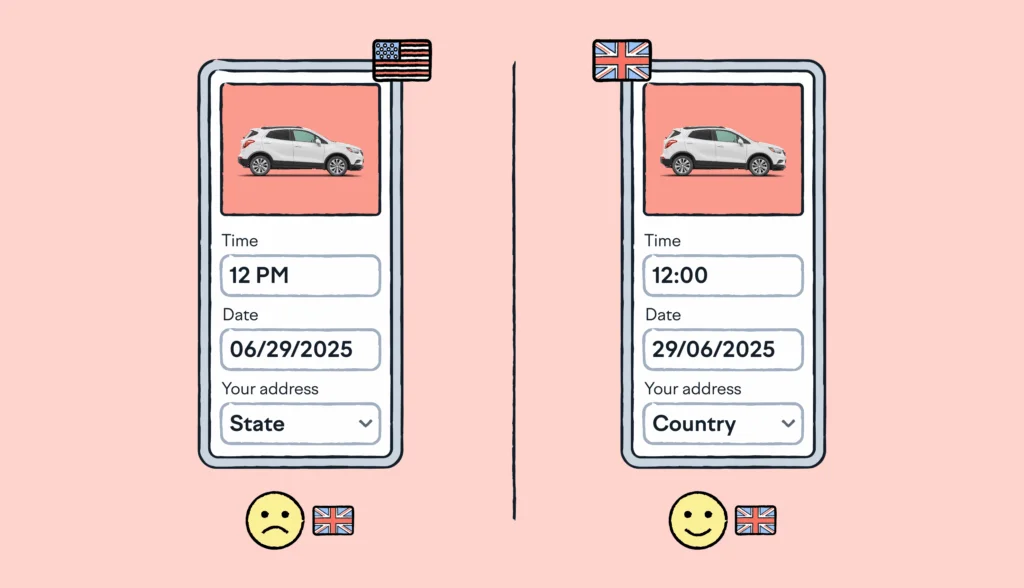
- Formatting standards: Formatting can vary across regions and become confusing. For example, date formatting is different in the US (MM/DD/YYYY) than in Europe (DD/MM/YYYY). You also need to consider the local conventions for time representations, number formatting, and currencies.
- Technical infrastructure: Account for geographical and regulatory differences in payments, privacy, content delivery networks, and other aspects. You want to choose the right string formats to present strings (text) in the appropriate manner for each language.
- UI and design: Plan design adaptation based on textual translation, especially when the content length is expected to increase (like when translating from English to German). You should build flexible layouts for these varying text lengths, focus on color symbolism, and imagery based on cultural nuances.
Many more factors come into play when working on the internationalization process. But these are the critical ones to prepare for.
3 real-world examples to help you make a decision
Looking for some real-world inspiration to choose between internationalization vs. globalization? These examples will clear up your mind.
1. Oatly
Strategy: Internationalization
Oatly is a Swedish oat milk producer.
The brand tailors its product formulation and packaging to different markets like Germany, the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, and more. They adapt manufacturing to use locally-sourced oats where possible.
The brand’s marketing also switches gears to resonate with consumers in specific markets. For example, it adopts a witty, humorous, and provocative tone in Western markets. But the messaging becomes more educational and health-focused in Asian markets where plant-based milks are not popular.
Oatly’s website is also localized for each target market:
2. BlaBlaCar
Strategy: Internationalization
BlaBlaCar is a ridesharing platform available in many countries. Since travel habits and behavior have many cultural variants, the brand customizes its entire business model across markets.
In Western Europe, it focuses on long-distance intercity travel. On the other hand, in developing markets, the brand introduced shorter commuter routes and different payment systems accommodating cash-based economies.
BlaBlaCar also follows different approaches for user verification or KYC based on local regulations.
3. Basecamp
Strategy: Globalization
Basecamp is a project management software. The company offers a standardized product and pricing model for all markets.
Rather than creating region-specific versions, the brand maintains a single, simplified product that works identically worldwide. It also offers a consistent flat-fee pricing without any regional variations. So, whether you’re in Bangladesh or Mexico, you’ll see the same price points.
Choose the right approach for your business
In essence, globalization and internationalization are two sides of the same coin of business expansion. As technology continues to blur geographical boundaries, understanding these concepts is critical for tech enterprises eyeing global domination.
Choosing between simultaneous global expansion and a phased approach depends on a business’s resources and risk tolerance.
If both sound intimidating, you can establish a physical presence through a subsidiary first. Or work with local partners to build viable paths for international growth. Either way, your success hinges on the ability to adapt to local markets and cultures.
Kickstart your global expansion
To help you follow in the footsteps of the 3000+ companies who’ve successfully localized, check out Global-ready growth, our guide to unlocking international revenue.
DownloadFAQs
What are the potential risks of internationalization for businesses?
Internationalization has a few challenges for businesses, such as:
- Complex regulatory frameworks
- Cultural differences and sensitivities
- Need for significant investments in infrastructure
Navigating these obstacles can be time-consuming, costly, and disruptive to a company’s organizational structure.
How can businesses adapt to local markets and cultures during international expansion?
Adapting to local markets and cultures is crucial for success. As part of a strong global marketing strategy, you might have to modify product offerings, marketing approaches, and pricing policies to align with local preferences and purchasing habits.
Hiring local staff, partnering with local companies, and investing in local knowledge and expertise are key steps to building strong relationships and positioning for long-term success in international markets.