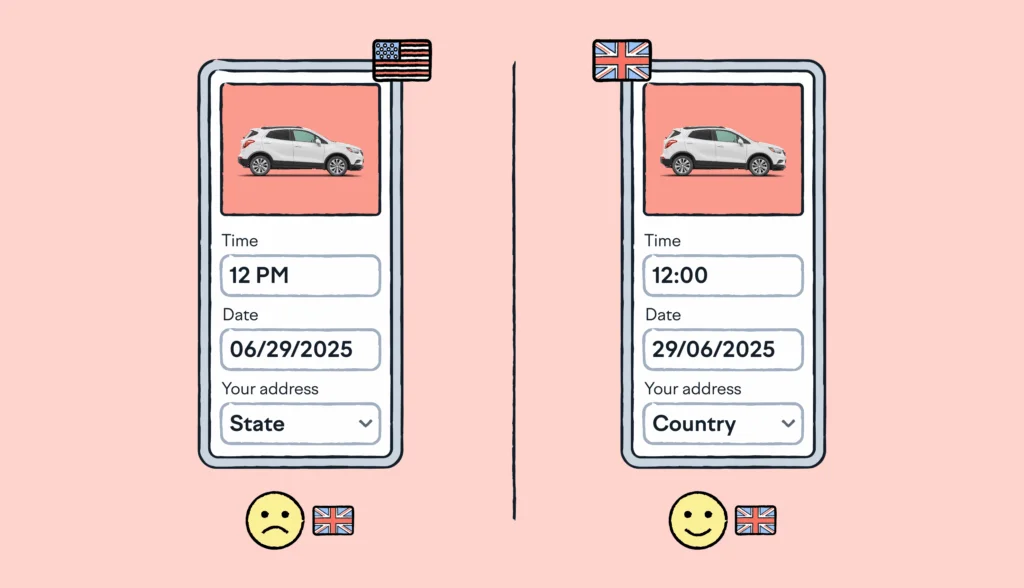
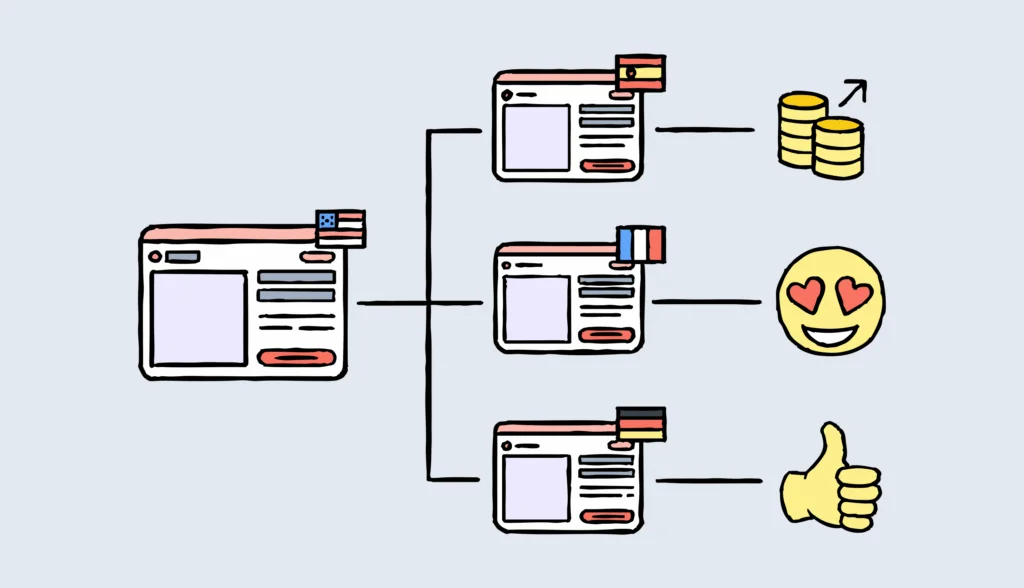
Expanding into global markets isn’t just about selling more. It’s about truly connecting with your customers.
A multidomestic strategy helps you achieve just that by tailoring products, services, and marketing to fit local needs. It’s the difference between being just another foreign brand and becoming a local favorite.
In this article, we’ll break down what makes a multidomestic strategy effective, explore its key benefits and challenges, and share real-world examples to help you decide if it’s something you should pursue.
💪 Zero-fluff content
To make sure you get straight to the insights you need, we’ve stripped away the unnecessary jargon and focused on practical, actionable information. We included real examples from companies such as Starbucks, Unilever, and Netflixs, so you can see exactly how multidomestic strategies work in practice.
Understanding multidomestic strategy
A multidomestic strategy takes a decentralized approach to international expansion, allowing companies to adapt their products, services, and operations to meet the unique needs of each market they enter.
Unlike a global marketing strategy, which focuses on offering standardized products worldwide, a multidomestic strategy emphasizes localization to resonate with specific locale.

In a nutshell, a multidomestic strategy potentially propels a company’s global presence, making it competitive in each local market. It has high local responsiveness, and it leaves no room for a one-size-fits-all methodology.
Global strategies have low local responsiveness and will generally prioritize economies of scale and a cost-efficient approach.
💡Pro tip: Balancing local autonomy with corporate oversight is important. It’s what gives your local experts the flexibility to adapt while still aligning with the company’s overall goals and brand identity.
Key components of a multidomestic strategies
To succeed with a multidomestic strategy, companies need to focus on a few essential steps that help them adapt to local markets, connect with customers, and stay competitive.
1. Establish a strong local presence
To truly connect with a market, you need strong relationships with local suppliers, distributors, and consumers. This means understanding their culture, language, and business practices.
Learning from Starbucks’ multidomestic strategy
In 2018, Starbucks in China partnered with Alibaba to offer delivery services and design stores that reflect Chinese traditions, which helped them connect with local consumers.
The coffee giant worked with Alibaba to make the most of their platforms like Ele.me for delivery and Hema supermarkets for localized operations. Additionally, they created a virtual store in Alibaba’s ecosystem, allowing customers to connect with the brand across platforms.

In 2018, Starbucks partnered with Alibaba as part of their multidomestic strategy efforts (source)
So, what can you learn from Starbucks?
- Collaborating with trusted local companies can help you break into the market faster
- Use local insights to customize your offerings, and make sure the experience you offer feels personal and relevant
- If you have the resources, meet customers where they are by integrating digital and physical experiences
But what if you don’t have immediate access to local partners?
2. Invest in market research and development
Success comes from understanding the cultural, economic, and regulatory landscape of each market. Yes, this takes time and resources, but it’s incredibly important for creating products and services that resonate.
Unilever’s “inclusive vision of beauty”
Unilever is a great example of redefining the messaging of their core product to take into account multiple markets. In a way, their multidomestic strategy prevailed their global one. The company has taken significant steps to promote inclusivity in its skincare portfolio.
Unilever removed terms like ‘fair,’ ‘white,’ and ‘light’ from product packaging and communications, and decided to rebrand products such as Fair & Lovely to align with a more inclusive vision of beauty.

Old Unilever product name “Fair & Lovely” was criticized for suggesting a singular ideal of beauty (source)
Unilever dominates the market in South Asia, with India having the largest market share, but does this messaging resonate with women of color? Not really.
What can you learn from this multidomestic approach?
- Realistically evaluate whether your messaging is excluding or offensive
- Be wary of product names and descriptions, and make sure your communications reflect the cultural values and sensitivities of each market
- Take proactive steps to address societal issues, such as harmful beauty stereotypes
We already touched upon marketing a bit, but lets take a closer look as it is extremely important for creating a strong multidomestic strategy.
3. Adapt your marketing and offerings
To resonate with customers, your marketing and product offerings must reflect local tastes and trends. This means you need to understand what matters most to each audience—whether it’s cultural preferences, lifestyle habits, or even how they engage with your brand.
How Netflix won over South Korea
Netflix’s success in South Korea highlights a smart application of a multidomestic strategy. The company decided to invest in Korean content (does “Squid Game” ring a bell?), and accomodate local payment preferences.
In April 2023, Netlix announced they’ll be investing $2.5 billion in Korean content over the next four years. It positioned itself as not just a streaming platform, but one deeply connected to Korean culture.
So, what lessons on multidomestic strategy does this bring to you?
- Understanding local tastes and preferences is key, so make sure to invest in localization
- Small adjustments, like offering region-specific payment methods, can remove barriers for customers and increase adoption
- Consider how your localized offerings can showcase your brand’s global strengths while aligning with local interests
💡Fun fact: Netflix’s “Squid Game” illustrates the benefits of free trade and globalization. It wasn’t just content for South Koreans. It turned out to be a global hit, proving that authentic, localized offerings can also resonate on a larger scale.
Challenges of a multidomestic strategy
While a multidomestic strategy has clear advantages, it also comes with its fair share of challenges. Local adaptation can add layers of complexity, create inconsistencies in your brand, and increase costs.
The good news is, once you’re aware of the challenges, you can stay agile and prevent mishaps. Here are the main ones.
Operational complexity
Managing operations across multiple markets isn’t easy. Each region comes with its own regulations, supply chains, and cultural nuances.
For instance, McDonald’s has to navigate different food safety standards across different regions, which can quickly increase compliance costs. Plus, training and managing employees across diverse cultures can make maintaining consistency even harder.
💡Pro tip: Depending on the industry and size of your organization, you might need to invest in robust systems and resources to handle these differences. For example, you could use local compliance management systems to navigate regulations, or communication platforms to keep global and local teams aligned.
Inconsistent brand image
Tailoring products and services for each market can sometimes dilute your brand’s identity. Customers may get confused if your offerings or messaging feel too different across regions.
Subway, for example, risks losing its global brand recognition if its menu varies too much between markets. Balancing local brand relevance with a cohesive global image and how the parent company is presented in other countries–can be extremely challenging.
Higher costs
Running operations in new markets is expensive. Lenovo, for example, has regional headquarters in the US, China, and Singapore to manage local operations. These setups require significant resources, from maintaining multiple supply chains to hiring specialized teams.
The result? Costs can add up quickly, making profitability a challenge without careful management.
Is multidomestic strategy the right approach for you?
Whether or not you need a multidomestic strategy is highly dependable on your market expansion ambitions. Check out the table below to discover five key questions to help you determine if it’s the right fit for your business.
|
Question |
Why it matters |
|
How diverse are the target markets I want to enter? |
Determine if there are any significant cultural, economic, or regulatory differences between the regions that would require tailored products, services, or marketing strategies. |
|
Can I afford the investment? |
Evaluate if you have the resources—financial, operational, and human—to support decentralized decision-making, multiple supply chains, and localized R&D. |
|
How much local autonomy can I provide? |
Explore how comfortable are you giving regional teams the freedom to adapt while maintaining overall alignment with my brand’s vision and values. |
|
Is customer connection a priority? |
Think about whether or not customizing your offerings and marketing for local customer preferences will help you build stronger relationships and improve customer loyalty. |
|
How much would I need to invest in localization? |
Do a competitor analysis to understand what are the localized approaches, and what do customers in these markets expect. |
Of course, expanding into global markets with a multidomestic strategy can be transformative if done right. The key is balance, and that’s easier said than done. You need to give local company branches the freedom to adapt while keeping your overall goals and brand identity intact.
Yes, there are challenges, like managing complexity and ensuring consistency, but these can be tackled with thoughtful planning and the right tools.
Remember, the heart of a multidomestic strategy is connection. And localization is the key to building that connection.
Kickstart your global expansion
To help you follow in the footsteps of the 3000+ companies who’ve successfully localized, check out Global-ready growth, our guide to unlocking international revenue.
Download