When we talk about translation, we’re not just referring to word-for-word substitutions. It encompasses the art of conveying ideas in different languages, making them accessible and engaging to new audiences.
As globalization expands our horizons, the need for various types of translations is becoming essential in industries such as healthcare, finance, and law.
So, fasten your seatbelts as we explore the diverse world of translation and its crucial role in bridging cultural gaps, facilitating global communication, and driving business growth.
Types of translation
Translation isn’t a monolith. There are many different types, each with unique requirements and challenges. The most common types include:
Literal (word for word)
Literal translation is the most simplistic and basic translation type. It focuses on translating individual words from the source text into the target language.
Because they don’t consider grammar or context, literal translations aren’t very accurate and can sound awkward or unnatural.
For example, if you translate “Tengo hambre” into English word-for-word, you get “I have hunger.” Even though we know what “I have hunger” means, it sounds awkward.
As you can see, literal translation is probably not the best option when you’re dealing with more than one word.
Free (sense for sense)
Rather than translating one word at a time, free translation conveys the meaning of whole sentences. Free translation gives translators more freedom to consider cultural nuances, use synonyms, and rearrange or rephrase the words in a sentence.
Because free translation prioritizes the meaning of a sentence over the original wording and order, it can produce much more straightforward, natural-sounding results.
Even though “Tengo” means “I have,” free translation focuses on the sentence as a whole rather than the individual words. So, “Tengo hambre” becomes “I’m hungry,” not “I have hunger.”
Literary
Literary translation involves translating creative works such as novels, poetry, and plays.
Literary translators must be linguistic experts and have a deep understanding of the source text’s artistic style and structure. They must be able to convey the author’s intended meaning, tone, and style in the target language.
For example, imagine a literary translator may need to translate a poem from Spanish to English. To maintain the original poem’s rhyme scheme and meter, they need to understand both languages and nuances of poetry.
Technical
Technical translation involves translating highly specialized text, like technology manuals and scientific reports.
Translators need a deep understanding of the subject matter to convey complex technical information in a way the target audience will understand.
For example, a technical translator may need to translate a user manual for a piece of software from Japanese to English. This requires an understanding of both languages, the software, and its functionality.
Medical
Medical translation involves translating medical documents such as patient records, research papers, and clinical studies. Like technical translation, it requires deep subject matter expertise.
Medical translators must have a strong understanding of medical terminology and ethical considerations surrounding medical practices. They must accurately convey medical information to healthcare professionals and patients.
For example, a medical translator may need to translate a patient’s medical history from French to English. They must understand both languages, medical terminology, and the patient’s medical conditions.
Legal
Legal translation involves translating legal documents and contracts. Translators must be able to convey legal concepts and terminology clearly and accurately.
For example, a legal translator may need to translate a contract from German to English. Legal translation requires an understanding of both languages, legal terminology, and the legal systems of both countries.
Financial
Financial translation involves translating financial documents such as annual reports, financial statements, and investor relations material.
Just like legal, medical, and literary translators, financial translators must understand financial jargon and regulations to provide accurate translations. They must also convey the information in a way that both individual investors and financial professionals can understand.

For example, a financial translator may need to translate an annual report from Chinese to English. This requires understanding both languages, financial terminology, and regulations in both countries.
Audiovisual
Audiovisual translation involves translating video content such as films, TV shows, and documentaries. Subtitling translations is a common example.
Translators must understand the target audience and language to provide translations that resonate with the audience.
For example, an audiovisual translator may need to translate a film from French to Spanish. This requires an understanding of both languages and the cultural nuances of both countries.
Localization
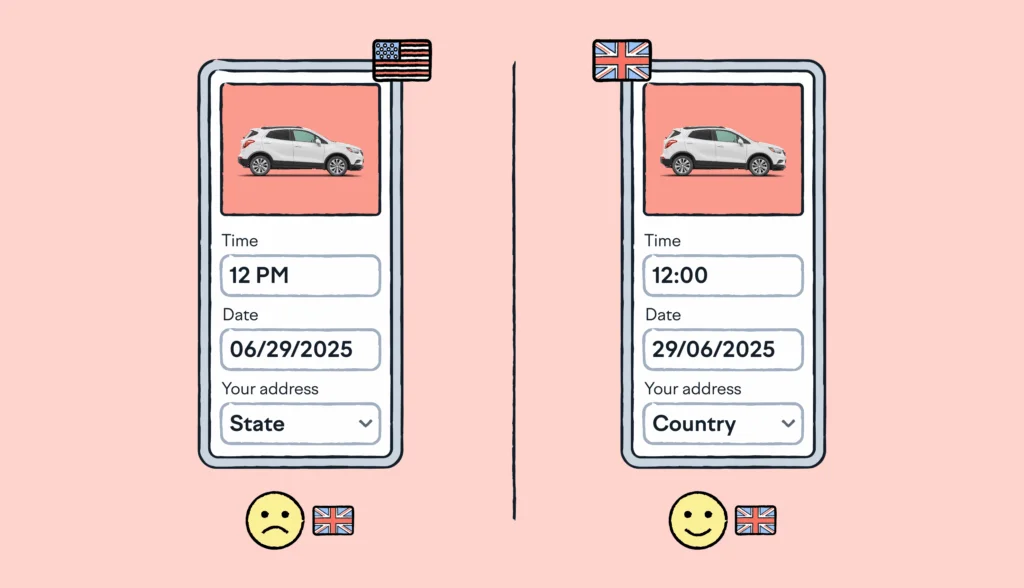
Localization involves adapting content to a specific geographic or cultural context. This includes translating language, images, and colors to ensure they are appropriate for the target audience.
The localization process ensures that content is translated and culturally adapted to resonate with target audiences.
For example, a company may need to localize its website for a specific country. To successfully localize content, you need to know the language, culture, and local preferences.
Transcreation
Transcreation combines elements of translation, creation, and copywriting. It allows creators to take apart an existing idea or digital asset, reimagine it, and transform it in a way that will resonate with target audiences.
Like localization, it takes social and cultural references into account to create something that sounds natural and feels familiar to consumers.
Understanding the importance of translation
Translation is more than just a helpful tool. It’s a universal key, unlocking global collaboration, innovation, and connection opportunities. By harnessing translation’s power, businesses can extend their reach and connect more deeply with their target audiences.
Bridging cultural and linguistic gaps
Culture shapes communication, and language is the vessel that carries it. Cultural and linguistic nuances are integral to the human experience, which means translation is no easy task.
Take literary translation, where words and phrases are heavily steeped in cultural context. Translating literature is about preserving and sharing our collective cultural heritage across centuries and borders. It allows audiences to connect with timeless themes and ideas through the genius of works like Shakespeare’s plays, Dante’s Divine Comedy, and Cervantes’ Don Quixote.
Reaching global audiences
On a practical level, translation is the lubricant of global communication, helping us overcome language barriers.
It’s not just about replacing words; it’s about transmitting meaning in a way that feels intuitive and clear to the target audience.
Imagine a SaaS giant translating its website into multiple languages or an e-learning platform that needs to create a new app with courses in dozens of languages. This expanded reach not only improves customer experience but also significantly boosts the companies’ bottom line.
A 2021 report by KPMG revealed that businesses expanding into international markets saw a 47% increase in ROI, showing the influential role of translation in business expansion.
Supporting business expansion and growth
But it doesn’t stop there. Companies looking to spread their wings into foreign markets need more than market knowledge. They must cater to the diverse cultures and languages of their target audiences.
Imagine a beauty product company looking to enter the Japanese market. Translating its website, product descriptions, and marketing materials into Japanese is crucial to establishing a strong presence and building a loyal customer base.
The 4 stages of the translation process
So, what does the process look like? It’s not a one-step operation but a careful, iterative journey that includes source text analysis, terminology research, translation and editing, and quality assurance and review.
Let’s break it down:
Source text analysis
The first step in this journey is analyzing the source text. It’s about understanding the text’s grammar, style, tone, and context.
For instance, if the text contains technical jargon, the translator must have the knowledge and language skills to translate these terms accurately.
Terminology research
Terminology research is essential to ensuring accuracy. Translators must identify the correct terminology to convey meaning effectively in the target language.
Specialized translation memory software can be invaluable, helping translators maintain consistency across multiple translations.
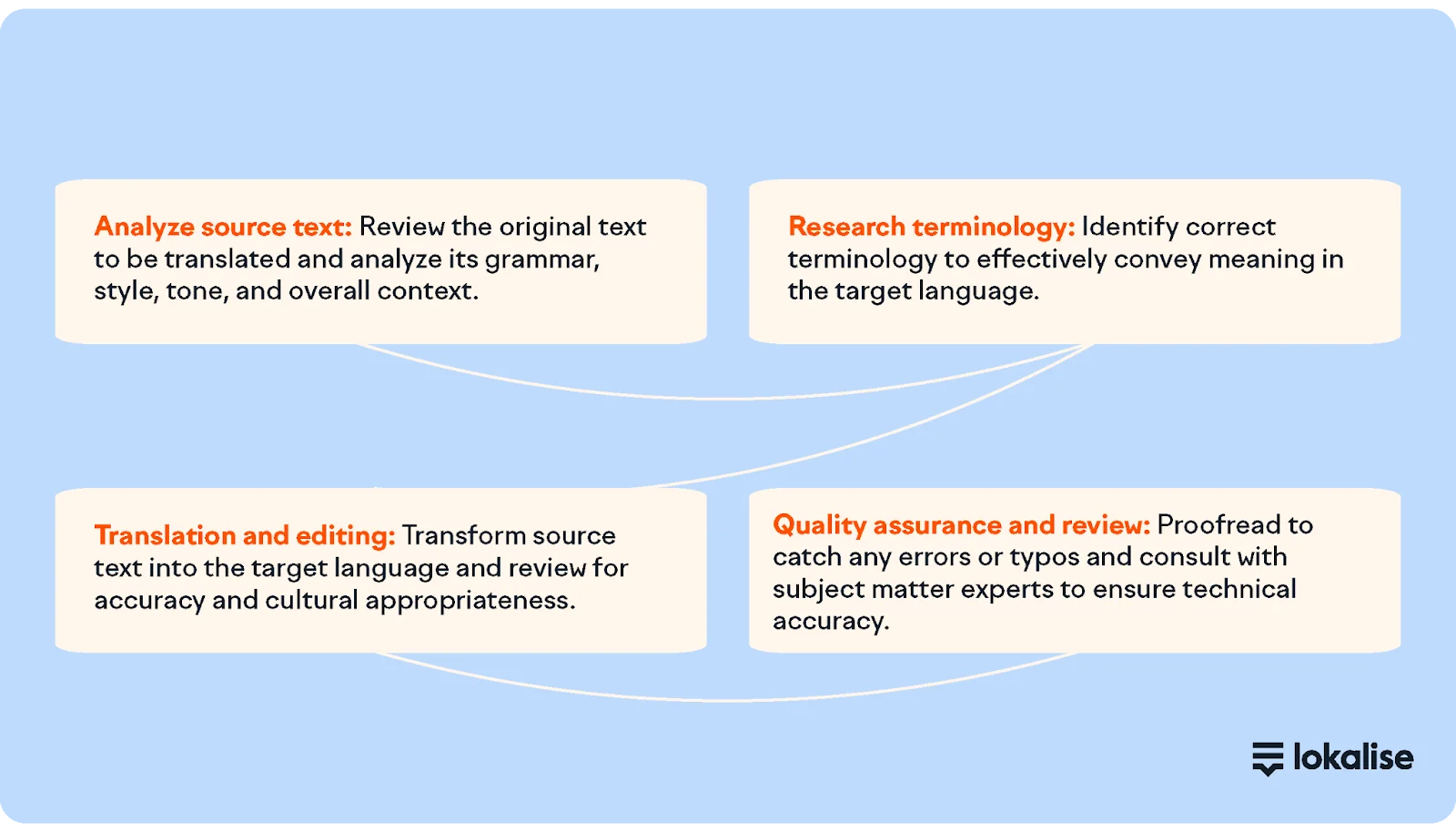
Translation and editing
The translation and editing phase is the crux of the process. During this phase, the source text is transformed, with careful attention to maintaining structure, tone, and style.
Cultural appropriateness is paramount here, especially when dealing with idiomatic expressions or cultural references.
During the translation and editing stage, the translator must pay close attention to the nuances of the target language and ensure that the translation is culturally appropriate.
For example, suppose the source text contains idiomatic expressions or cultural references that don’t make sense in the target language. In that case, the translator must find an appropriate equivalent that conveys the same meaning.
Quality assurance and review
Quality assurance and review are the final steps in the translation process. You review and proofread in this phase to ensure the translation meets your quality standards. Translation memory software, subject matter experts, and a keen eye for detail are essential.
During the quality assurance and review stage, the translator may use different tools and techniques to ensure the accuracy and quality of the translation. For example:
- Using translation memory software to ensure consistency across multiple translations
- Consulting with subject matter experts to ensure technical accuracy
- Conducting a final proofread to catch any errors or typos
The translation process is complex and iterative, requiring careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the source and target languages.
By following these stages and using the appropriate tools and techniques, translators can produce high-quality translations that accurately convey the meaning and intent of the source text.
Expand your reach with Lokalise
Translation is a complex yet profoundly vital part of our world. Whether it’s about bridging linguistic gaps, facilitating global communication, or supporting business growth, translation has a crucial role.
Knowing the types of translation and the expertise each requires, businesses can ensure they’re putting their best foot forward in the global arena. Success is more than translating words — it’s about capturing the meaning behind them in a tone that’s just right for your audience.
FAQs
What is the importance of cultural and linguistic nuances in translation?
Cultural and linguistic nuances are crucial in translation as they shape how we communicate and convey meaning. Translating literary works, for example, requires preserving the cultural context and ensuring the message resonates with the target audience.
By capturing these nuances, we can connect across borders and appreciate different cultures’ timeless themes and ideas.
How does translation contribute to business expansion and growth?
Translation plays a significant role in business expansion by allowing companies to cater to diverse cultures and languages. Translating a website can help brands establish a strong presence in foreign markets and build a loyal customer base.
Whether product descriptions, marketing materials, or video games, translating content into a customer’s native language increases their chances of converting. It’s a strategic move that supports business growth across industries.