What is a transnational strategy
A transnational strategy is a business approach that balances global consistency with local adaptability. It focuses on standardizing key operations, like branding and production, while customizing products, services, or marketing to meet the unique needs of local markets.
Let’s say you’re running a chain of restaurants across different countries. You keep the same core menu and standards (so everyone knows it’s your brand), but you tweak some dishes to match local tastes. For example, you might add spicier options in Mexico or offer vegetarian dishes in India.
Key components of a transnational strategy
A transnational strategy combines the best of global efficiency with local adaptability. It has three main components.
Centralized global operations
Transnational strategy prioritizes centralized operations for efficiency. Think supply chains, production, and branding. At the same time, businesses will allow for local tweaks, like adapting marketing campaigns or product offerings to satisfy specific markets.
Standardization with customization
International companies will likely standardize core elements of their products or services that don’t need to change. This typically includes the brand identity or key features, if we’re talking about software. However, they will customize what matters to local customers (e.g., flavors, packaging, service models, international pricing strategies).
Integrated global management
While a global team ensures overall strategy and alignment, teams working in local branches have the autonomy to make decisions that address the needs of every country. This structure allows businesses to move quickly and respond to regional demands without losing sight of the bigger picture.
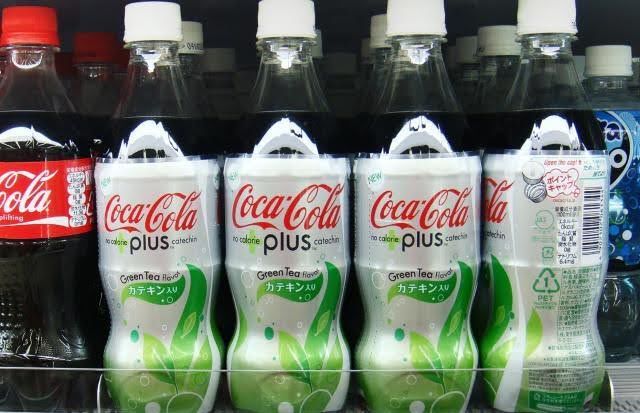
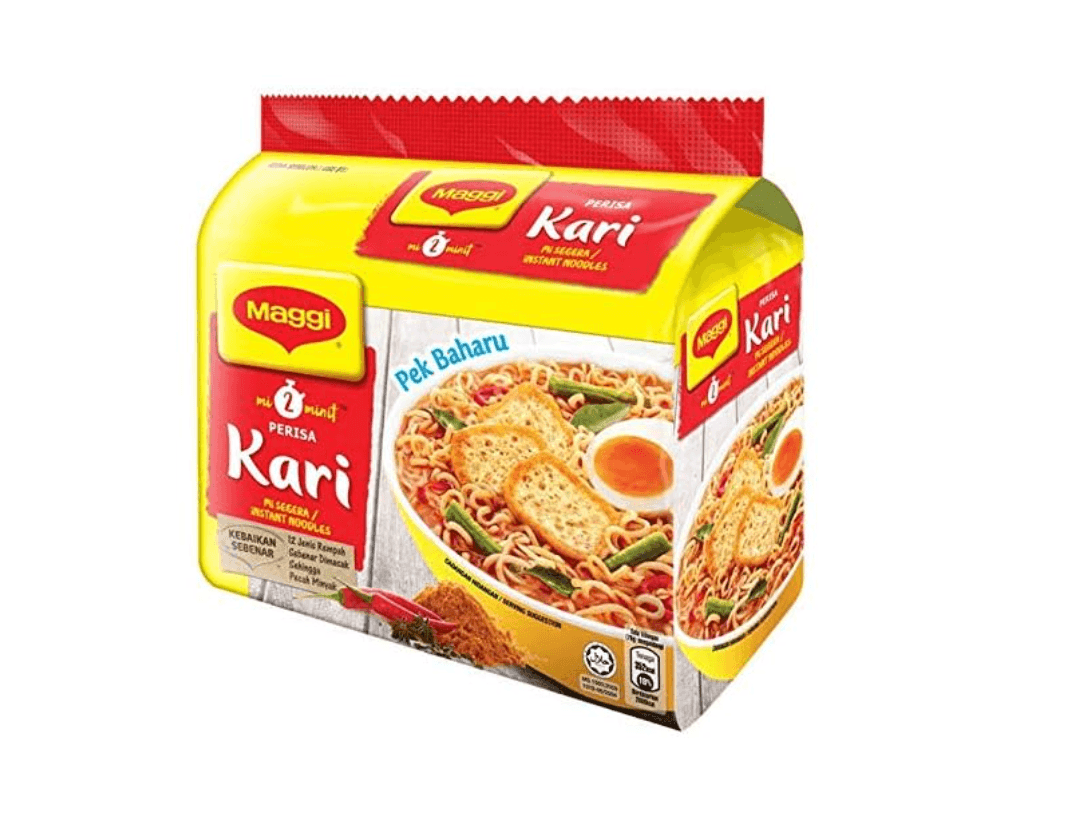



 Curry flavored Maggi noodles adjusted for the customers in Malaysia
Curry flavored Maggi noodles adjusted for the customers in Malaysia 
