How AI translation works
AI translation works by using artificial intelligence to read a sentence, understand what it means, and then rewrite that meaning in another language. There’s a lot of sophisticated technology making that happen.
Let’s break it down in a way that’s easy to understand.
Step 1: The model learns languages
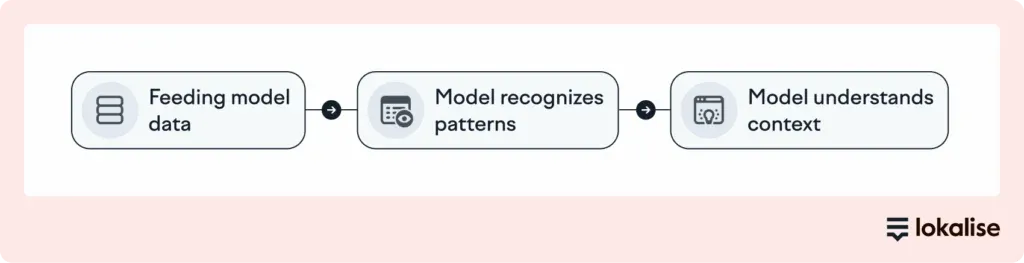
AI translation starts with training a model. Imagine you’re teaching someone to become fluent in multiple languages, but not by explaining grammar rules. Instead, you’re showing them millions of real-world examples. That’s exactly what happens.
The model is fed massive amounts of bilingual or multilingual data. Think websites, books, subtitles. This is how it learns patterns, sentence structures, and vocabulary across different languages.
Over time, the model doesn’t just memorize word pairs, but also starts to understand how meaning is shaped by context, word order, and nuance.
Step 2: Turning words into numbers
Here’s where the AI part kicks in. The model doesn’t “see” words the way we do. It converts each word (and sometimes each character) into a vector. A vector is a long string of numbers that capture the meaning and relationship between words. This is called embedding.
For example, in English, the words “cat” and “kitten” will have similar vectors because they’re related. The same goes for their equivalents in other languages.
Step 3: Encoding the sentence
Once the words are turned into numbers, the model runs them through a thing called an encoder. You can think of this as the part of the system that reads and understands the source sentence. It looks at the entire sentence, not just word by word, and creates a kind of compressed summary of its meaning.
Step 4: Decoding into another language
Then comes the decoder. This is where the magic of translation occurs. The decoder takes the compressed summary and starts rebuilding the sentence in the target language. It does so by looking at the entire meaning and predicts the next best word, one by one, until the sentence is complete.
Step 5: Adding context with an attention mechanism
To make translations more accurate, modern systems use something called an attention mechanism. Think of it like a spotlight that helps the model focus on the most important words or phrases in the original sentence while it’s translating. This is why AI translations today are much better at handling longer, more complex sentences than older machine translation systems.
Step 6: Continuous learning
AI translation models don’t stop learning once they’re built. They continue to improve after they’re launched by analyzing new data, spotting mistakes, and adjusting their translations. For example, if enough people correct the same translation over and over, the model can learn from those corrections and avoid making the same mistake next time.