What is globalization?
Globalization is the process of expanding business operations across international markets to reach a global audience. Digital connectivity has made markets accessible, and AI-enabled market entry has made international expansion affordable for businesses. This underlines a shift in globalization from being a capital-intensive endeavor to a strategic play for businesses of all sizes.
The ultimate goal of this process is to make it easier to do business beyond domestic borders.
For businesses, globalization unlocks access to global markets and creates systems to operate in them. It requires brands like yours to adapt your product/service, content, and experiences for different languages, cultures, and regulatory environments.
G11n framework (Globalization) = i18n (Internationalization) + l10n (Localization)
Globalization (G11n framework) is a byproduct of internationalization and localization.
Let’s understand these concepts to learn how.
- Internationalization (i18n): The practice of designing your product/service to support multiple languages and regions without requiring re-engineering later.
- Localization (l10n): The practice of adapting your product/service for a target market by translating content and tailoring the customer experience.
- Globalization (g11n): The process of expanding into new markets with the support of an internationalized product and localized content.
Think of it like building a house. Internationalization is the process of creating the foundation. Localization is the process of fitting out each room. And globalization is the entire project from architecture to move-in day.
Globalization 3.0: Understanding the impact of AI
For decades, globalizing a business required a massive budget. A lot of costs went into international expansion, including hiring translators and local teams, establishing legal entities in every market, and managing costly vendor relationships.
That meant only well-funded companies could afford to invest before proving demand.
But AI adoption has significantly shrunk these costs and changed the economics of business globalization.
Your AI-enabled market entry plan looks like:
- Market validation: Use AI tools to scan search behavior, conduct user research, and validate demand in days instead of weeks.
- Localization: Tailor UI copy, marketing collateral flows, and brand messaging to local customers.
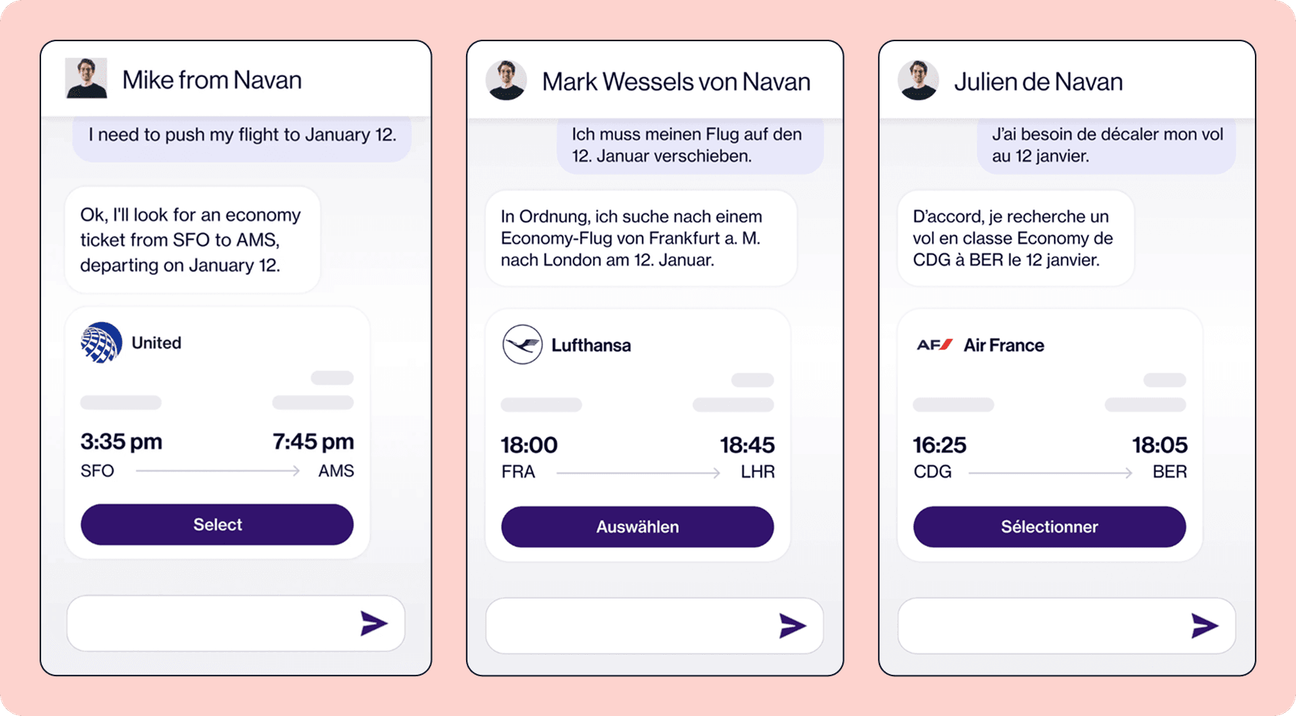
- Customer support: AI agents can now handle real conversations, in multiple languages, across chat and voice.
- Sales and marketing: Generate and adapt landing pages, ads, emails, SEO content, and social posts for every market at a fraction of the cost.
In other words: The growing influence of AI has removed the cost barrier to globalization.
Businesses of all sizes can test the waters and enter global markets without a large upfront capital investment.
What are the advantages of globalization?
Globalization unlocks growth opportunities that weren't possible when businesses were confined to domestic markets. For companies considering international expansion, the benefits extend beyond revenue.
Let’s break down a few critical benefits of globalization.
Expansion into other markets
Businesses can reach larger audiences, diversify revenue streams, and reduce dependence on any single market. For customers, this means more choice, better quality through competition, and often lower prices.
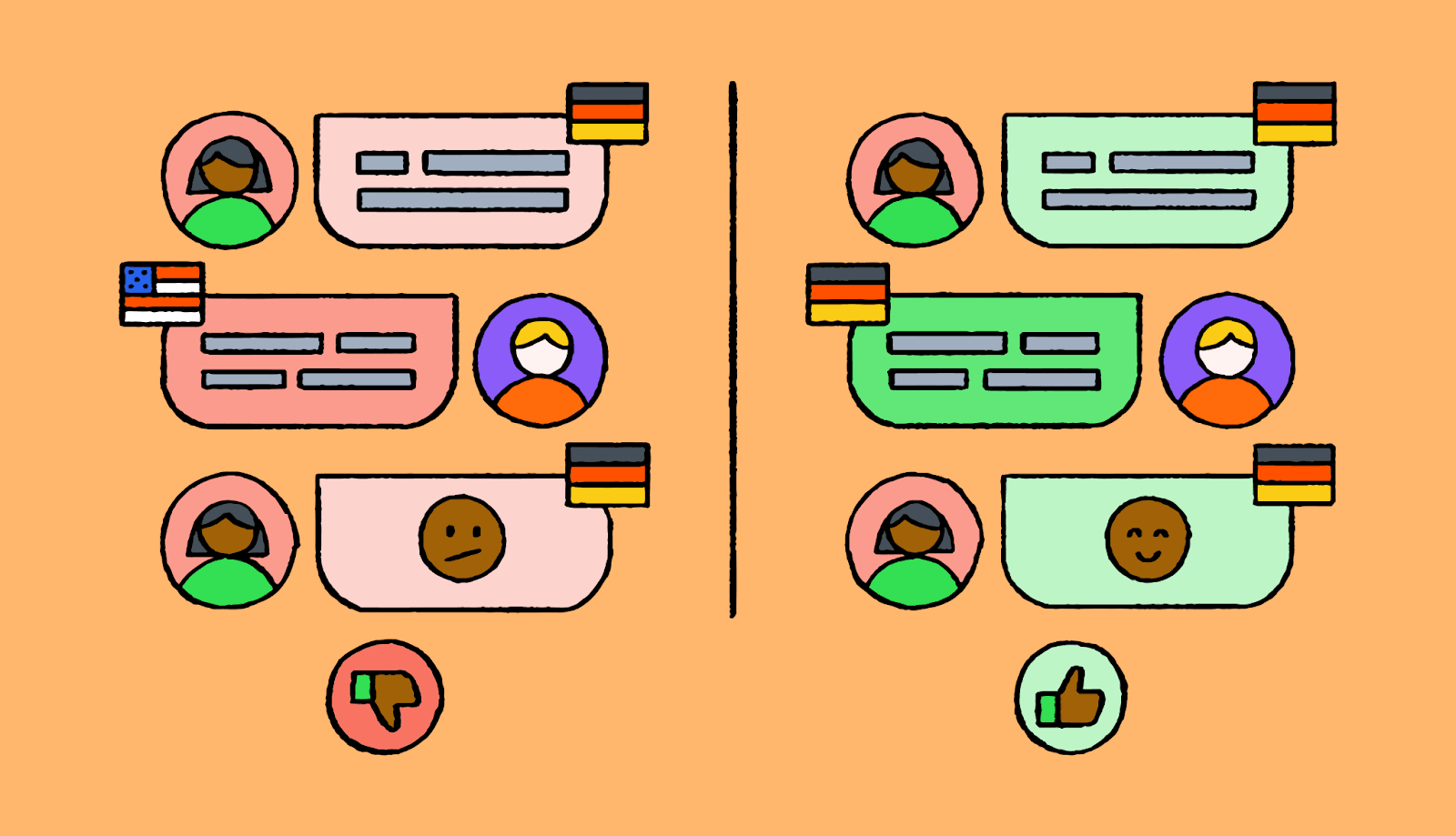
The language barrier is shrinking
Communicating with customers in their native language used to be expensive and slow. But AI-powered translation and modern localization platforms have made multilingual experiences accessible to companies of all sizes.
That means businesses can create personalized experiences in dozens of languages without enterprise-level budgets.
Global talent, distributed teams
More and more companies now operate remotely and hire globally. This allows them to tap into a vast pool of talent, bringing diverse perspectives and skills to the table. Some countries are also making it easier for digital nomads to work remotely through temporary visas.
Seamless knowledge-sharing
Open borders speed up the transfer of technology and ideas. Cross-border collaboration also leads to breakthroughs that no single country could achieve alone, including ideas like open-source software development. When knowledge flows freely, innovation compounds.
What are the disadvantages of globalization?
Globalization doesn’t have all the answers. Where the scales tip in favor of economic growth and technological advancements, they weigh heavily with concerns over economic inequality and environmental issues.
Let’s go over some of these downsides in more detail.
Data sovereignty and digital borders
The internet may be global, but data regulation is increasingly local. Alongside the EU's GDPR, dozens of countries have their own data protection laws today. Many require data to be stored and processed within national borders.
For businesses, this means you can't simply copy your domestic setup into a new market. You have to focus on legal review, localized privacy policies, and, at times, create separate infrastructures.
Cultural homogenization
When global brands dominate in a market, local players often struggle to compete. This raises legitimate concerns about cultural erosion. It could lead to the flattening of local identities, traditions, and languages as markets converge around dominant players.
Supply chain vulnerabilities
Stretched supply chains make the world more susceptible to disruptions. Whether disruptions are man-made or natural, it’s clear how quickly interconnected systems can break down.
When going global, companies have to think about supplier diversification to protect themselves from issues in the chain.
4 signs your business is ready to go global
Globalization is a growth lever, but only if your business is ready to pull it. Expanding too early stretches resources thin. Expanding too late means ceding ground to competitors. The key is recognizing the signals that suggest now is the right time.
Before you reach for the whiteboard and start planning your globalization strategy, spend some time weighing these factors to assess your readiness.
1. You have organic demand from non-domestic markets
The clearest indicator of globalization is seeing strong signs of organic demand. This could look like website traffic, signups, orders, downloads, and support queries from regions you haven't targeted.
These users are finding you despite any conscious effort to reach them. You can scale these numbers by investing more in them.
2. You have a stable core product or product-market fit
One prerequisite for business globalization is a stable core product. If you're still iterating heavily on core features, localization will multiply your workload with every change.
When you have a stable foundation (or, in the best-case scenario, product-market fit), international expansion becomes more manageable and focused. You won’t waste time on breaking and fixing things frequently.
3. You have a clear international revenue opportunity
Expanding globally can seem like the next big leap to many businesses, but it’s not always the best move.
Establishing a clear revenue is a decisive factor for your globalization play. Look at whether competitors are succeeding in your target markets. Are their pricing models and structures translating well? Is the addressable market large enough to justify the investment?