Poor localization leads to a bad user experience, brand erosion, costly and embarrassing mistakes, and potential legal issues.
Deprioritizing localization quality = deprioritizing customer experience.
This should be the message you get across to other stakeholders when talking about the importance of localization quality assurance (LQA).
Before explaining the best practices and how to do LQA to improve the quality of localized content, let’s go over some basics of localization management to understand how quality assurance fits into the broader process.
What is localization quality assurance (LQA)?
If translations, design, and functionality don’t work for your intended audience, customers are not going to engage or convert.
That’s why you need to check the quality of your localized products and services to make sure they meet the expectations of your target market.
This process is known as localization quality assurance (LQA). It makes sure content fits your target audience’s cultural, demographic, regional, and functional preferences.
|
Localization quality assurance (LQA) |
|
|
Language checks |
Linguists or translators proofread texts to spot any spelling, grammar, syntax, punctuation, formatting, and consistency errors. They look at both translated text and source or original text. |
|
Cultural relevancy |
Localization experts check that products, services, texts and visuals, meet the cultural, social, and legal norms of the target markets. |
|
Technical compatibility |
Localization engineers and designers test products and services to make sure they’re appropriate for the audience and compatible with local systems. |
In short, testers and linguists meticulously review localized content, comparing it with the original. They do so to identify and correct errors, inconsistencies, or potential issues that may arise from specific nuances, cultural differences, or behavioral norms.
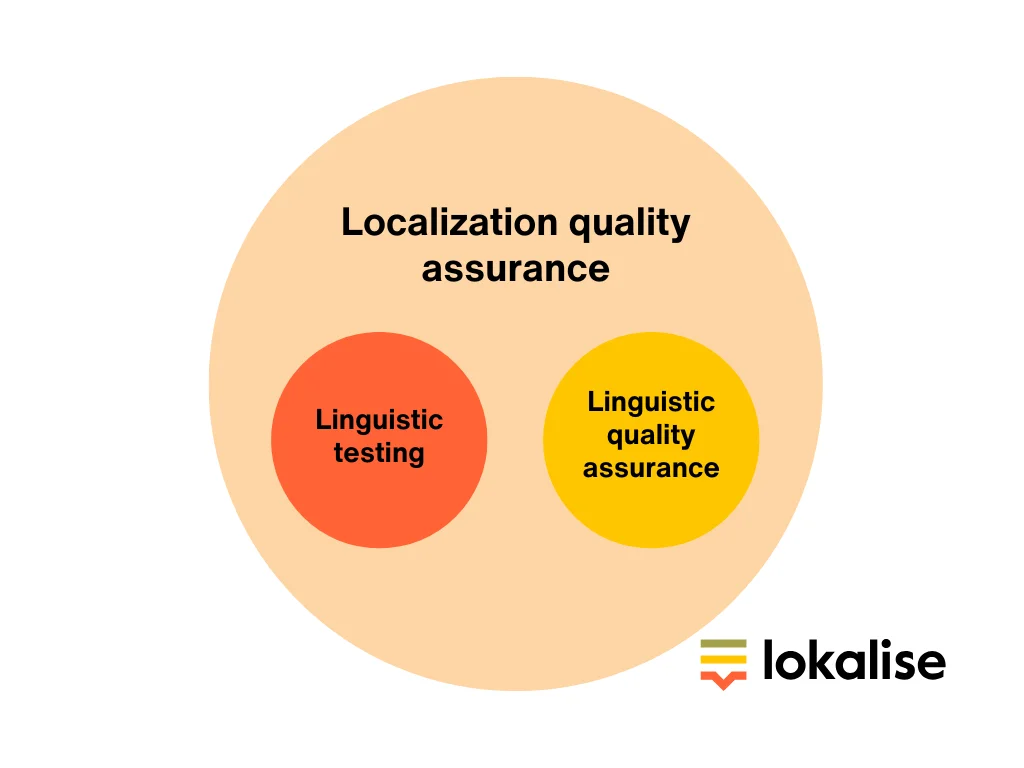
Linguistic vs localization quality assurance
Let’s first get the terminology straight.
Linguistic quality assurance is only one part of the localization quality assurance process.
As a matter of fact, there is a difference between the linguistic testing process, linguistic quality assurance, and localization quality assurance, but they are all equally important.
Let’s take a closer look.
Linguistic testing
Linguistic testers will check the language functionality within a specific environment, such as software, websites, or mobile apps. Through functional testing, they can make sure that the translation displays correctly and functions as intended in the localized version of the product.
They might test things like:
- Text truncation
- Encoding issues
- UI layout (e.g., whether text fits in buttons or fields)
- Implementation of translated strings in the user interface
Linguistic quality assurance
Linguistic quality assurance is a broader process. Here, you’re testing the quality of the translation itself, independent of its display or functionality. This includes checking for:
- Grammatical correctness
- Consistency
- Terminology accuracy
- Adherence to the style guide
Localization quality assurance
Localization Quality Assurance (LQA) is a comprehensive process that goes beyond linguistic quality assurance and linguistic testing. In fact, it combines both aspects so that the overall quality of a localized version of the product is on point.
In a nutshell, LQA checks how well the product is adapted for the target market in terms of functionality, cultural relevance, and user experience. Localization testing will look at:
- Usability of the product in foreign markets
- Functionality and design
- Cultural adaptation (e.g., visuals, symbols, and color choices are culturally appropriate)
- Adherence to localization standards (e.g., legal, regulatory, or compliance standards)
The end goal is to make sure the product functions well and that the user experience feels native to the audience.
Your localization quality assurance program in 6 steps
Localization quality assurance is not something you can rush. The more meticulously you prepare for your LQA process, the smoother it will be, and the higher the quality of your localization.
To check that a product, service, texts, and visuals have been localized correctly and at a high quality across different cultures, here are the steps you should follow:
1. Prepare for localization quality assurance
First, you need to do some pre-planning. Here’s a checklist of all the things you need to do as you prepare for the localization quality assurance process.
- Define your quality and style guidelines
- Choose your QA team
- Choose the right tools
- Prioritize what you’re going to test
- Set KPIs for localization
- Create the LQA process timeline
Let’s go over each of these.
Define your quality and style guidelines
Quality can be defined in many ways. You need to define where’s the quality bar and to hold all team members accountable to it.
Create a style guide, translation glossaries, and QA checklist for your content. These will act as reference tools for your translators and testers, helping to keep consistency and quality across translations.
Choose your QA team
Your LQA team also needs to understand the culture of your target market. Variations in dialect and cultural expressions can cause serious communication gaps, so they need to be able to capture these.
Even though some markets speak the same language, they use different expressions:

LQA testers are usually experienced linguists and localization experts who have a deep understanding of the target languages and cultures and are proficient with QA tools and processes.
But you’ll likely need to call in other experts, depending on your project:
- Localization engineers will need to handle any technical elements of the localization quality assurance process
- Designers will need to assess things like images, alignment, and layout.
- Subject matter experts might come in handy, especially if you’re operating in a highly-regulated industry (e.g., a medical expert if you’re localizing medical texts)
Choose the right tools
Your team needs access to tools and technology that make LQA processes efficient. Think CAT tools, tools with Translation Memory (TM) and translation glossaries, which not only speed up the translation process but also ensure consistency.
It’s useful to pick a solution with built-in translation quality assurance tools to track issues, but you also need to be able to manage workflows, and generate quality reports.
|
💡Pro tip We invite you to try Lokalise as you evaluate localization tools. Lokalise is a translation management platform that includes fully automated translation quality reviews. You can also assign them for a human review. Either way, you can upload your glossary and style guide for linguistic quality assurance checks that are on-brand and consistent. |
Prioritize what you’re going to test
You might decide to QA test a portion of your content, either because you don’t have the budget to test everything in one go, or because you want to launch a beta version as quickly as possible. Either way, you’ll want to prioritize, focusing on high-priority areas such as legal documents, business-critical texts, and UI elements.
Set KPIs for localization
Set quantifiable metrics to help you understand the performance of your localized content. You might want to measure customer engagement, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction. You should also measure the quality of your translations, this could include error rates, the accuracy of translations, adherence to style guides, etc. These metrics are essential for evaluating and refining your overall localization strategy.
Create the LQA process project timeline
Establishing the project duration and having clear milestones helps you complete each aspect of the LQA process within the designated time frame and manage resources effectively.
You might set up project milestones for the point when all initial translations are finished, the stage where all localized content has been checked and approved by your LQA team, or the beta release.
2. Start the localization quality assurance process
In this step, the quality of localization is tested for linguistic accuracy, cultural preferences, functionality, and cosmetic.
Linguistic and cultural testing
Linguists and localization experts focus on the linguistic quality assurance part of the localization testing process. They check the use of grammar, spelling, punctuation, syntax, idioms, style, and other linguistic elements. As they go through the localization quality assurance process, they might ask questions like:
- Do translations have the same meaning as the original text?
- Is there translation consistency?
- Are translations too literal?
- What are the cultural and contextual factors I need to consider?
- Are there any spelling variations, regional differences, and cultural nuances?
- Does grammar and syntax vary between target languages, even those that are similar?
- What punctuation rules should I follow?
- What are the stylistic rules for capitalization and the use of pronouns or adverbs?
- What are the appropriate formats for dates, distances, currencies, or times?
- Are cultural references familiar (books, famous figures, songs, etc.) and relevant to the target audience?
- Are date, number, address, and phone number formats correct?
- Has the correct symbol or units of measurement been used?
Creating a style guide can help you avoid linguistic errors in the first place, so always make sure you share style guides with translators before they start localizing.
Functional and technical compatibility testing
Localization engineers check if the localized version of your product or website works as intended in the target locale environment and is compatible with local systems and software.
They will make sure there are no broken links or buttons, that text displays correctly, and forms, scripts, and other interactive elements work as they should.
Here are some areas localization engineers will focus on:
- Website functionality: testing the website’s usability, including searching for products, purchasing, customer support, and navigating through terms and conditions. Identifying any issues or roadblocks that may interrupt the user experience
- App performance: all elements, such as buttons, links, menus, and dialogue boxes should function as expected. Text should be properly displayed without overlapping or being cut off, and in the right order (especially for languages written right-to-left).
- Compatibility: Products should operate without issues across different devices, operating systems, screen sizes, and orientations (landscape or portrait mode), and be compatible with local systems and platforms, like payment methods.
|
💡Pro tip Whenever possible, try to get feedback from native speakers. Product teams and engineers should always listen to local feedback and address any issues or suggestions users may have. Their perspective can help fine-tune the localization. |
Design and UX testing
Designers should do quality assurance and test the layout, alignment, fonts, colors, images, and any other visual elements of localization. This is important to make sure that design elements are culturally acceptable.
Every detail counts when it comes to the look and feel of your localized product, so each of these elements plays a significant role in ensuring a high-quality localization:
- Images and graphics: the use of metaphors, colors, icons, symbols, and imagery vary between cultures.
- Layout: check that the layout accommodates longer text. For example, German, Italian, and Russian have a longer average word length, reaching up to 30% longer.
- Font and encoding: Different languages may require specific fonts or encoding formats. Consider the visual presentations to ensure that fonts are easy to read and appropriate.
- Directionality: Some languages flow in a different direction compared to the source language. Ensure that text is directed appropriately, considering the reading patterns of the target language. This includes adjusting text alignment, navigation, and overall visual flow.
- Text Display: All text should be properly displayed without overlapping, truncation, or being cut off. It should also appear in the correct places and in the correct order, especially for languages that read right-to-left like Arabic or Hebrew.
- Buttons and Links: All clickable elements should be clearly identifiable, properly labeled, and large enough for easy interaction.
- Spacing: There should be appropriate spacing between lines, paragraphs, and different elements on the page for readability and a cleaner look.
|
💡Pro tip Take encoding requirements into account to avoid any issues with displaying non-Latin characters, which you’ll come across in languages with unique writing systems, like Chinese, Russian, Japanese, and Greek. |
3. Evaluate customer experience with a test run
OK, so the hardest part is out of the way. What’s next?
Before reaching the final review stage, it’s a good idea to do a test run with some of your customers.
This trial and error approach helps you identify potential issues in a controlled setting, preventing them from escalating when the content is released.
This stage is iterative and should be repeated until content is error-free and meets the quality standards you set at the beginning.
4. The final review
After all the changes have been applied, you need to do a final review. This final step in the localization quality assurance process ensures that no error was overlooked in previous reviews.
Check to see that improvements added value, didn’t introduce new issues, and that they align with the initial project objectives.
When you’ve confirmed that the localized content is error-free and ready for end-users, you can start preparing it for release.
5. Release and post-release monitoring
After the final review, the localized content or product is released for use by the end-users. However, the work does not stop there.
Post-release monitoring needs to happen. You need to collect user feedback and usage data, so that your team can swiftly identify and rectify any unforeseen issues that may arise. This continuous monitoring helps maintain quality and user satisfaction.
6. Create a localization quality assurance report
Finally, you’ll need to create a localization quality assurance report outlining changes made, areas for improvement, and giving evidence to support recommendations from your LQA team. The quality assurance report not only serves as a reference for the current project but also offers valuable insights for future localization efforts.
Let’s break down what you’ll see in your report:
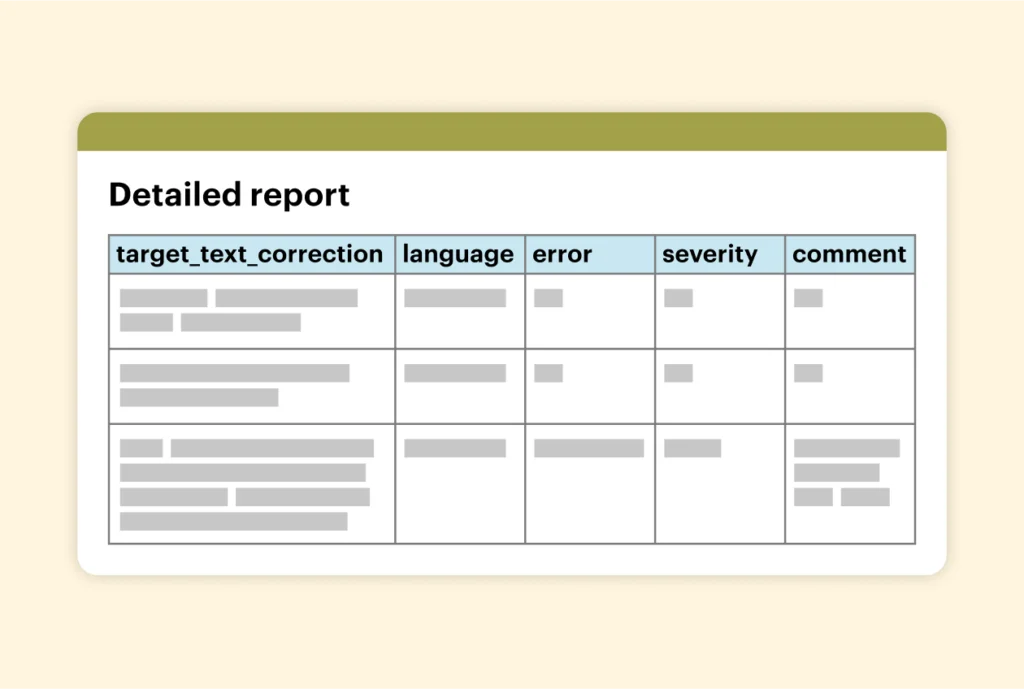
Each language will be displayed on a separate sheet in the report.
At the top, you will see the quality metric scorecard with all the detected errors. Here are some of the metrics you should pay attention to:
- Evaluation word count: number of words that have been evaluated for this language.
- Max score value: maximum quality score that a language can get. The default value is 100.
- Threshold value: the quality score threshold that determines whether translation quality for this language passed or failed. The default value is 85.
- Overall quality score: primary quality measure for your translations.
- Pass/fail rating: indicates whether the quality score has passed the threshold or not.
Below the scorecard, you’ll also get a detailed report that shows the exact errors. Besides error and severity level, you can also see:
- Suggested correction: the AI will provide a corrected translation to fix the issue.
- Comment: the AI explains why it has flagged this as an error.
A localization quality assurance report serves as a powerful tool for continuous improvement. You’ll need to regularly collect feedback, learn from your mistakes and successes, and continuously refine your LQA process based on these learnings.
Is localization quality assurance worth the investment?
Absolutely. Localization quality assurance is a worthwhile investment for businesses expanding into global markets. By making sure that their content is accurate, culturally relevant, and functional, companies can improve user experiences, establish credibility, and build trust in new markets, all of which contribute to a stronger localization ROI.
So, again yes, LQA is worth it, and here’s a quick summary of why:
- More accurate and culturally appropriate translations
- Improves engagement and click-through rates
- Keeps customer satisfaction high
- Builds brand credibility
- Gives you more confidence to expand into new markets
- Improves the overall localization process
Believe it or not, but you can also automate parts of your localization quality assurance with Lokalise AI.
The tool is built on OpenAI’s GPT API, which helps it automatically identify linguistic issues, categorize them, and then deliver detailed reports with comments and suggested corrections back to you.
The best of all? It takes just a few minutes to complete. Learn more about Lokalise AI–the benefits exceed just quality assurance.