Selling globally can significantly increase revenue, but only if you localize your ecommerce platform properly.
You might have taken the first steps of translating your ecommerce platform into a few languages to support product promotion efforts.
But hesitated to go any further because of the perceived complexities of localization.
But here’s the thing. Ecommerce localization doesn’t have to be that difficult.
Webinar catchup: ecommerce localization
Catch up on our webinar in partnership with Hygraph: Mastering the art of ecommerce without borders, with localization experts Jenn Alvin and Aaron Presley.
Save your spotIf you know the key elements to consider, how to choose the right tools, and how to set up an efficient ecommerce localization workflow, you’ll find that it’s pretty easy.
For reals!
This guide will help teams like developers, product managers, and marketers launch and optimize localized ecommerce experiences.
What is ecommerce localization?
Ecommerce localization involves more than translating your store. It’s the process of adapting your existing store to fit the shopping experience of each of your target markets.
This means updating elements like pricing, currency, payment options, product descriptions, delivery information, UX, design, SEO, managing localization costs and so much more. You’ll also need to consider cultural sensitivities, like themes, colors, traditions, and symbols. What’s acceptable in one region could offend in another.
In short, every detail matters to make sure your store looks and feels just right.
Why bother with ecommerce localization?
Language is one of the most personal ways you can connect with customers.
CSA Research found that 76% of online shoppers prefer to purchase products in their native language.
Going multilingual is fast becoming a key personalization strategy for businesses expanding into several markets.
Not only will you reach more people, but you’ll also send a powerful message.
That EVERY SINGLE customer deserves to be served in their mother tongue.
You’ll build trust too. Customers will be able to spot content that hasn’t been properly localized from a mile off because it won’t feel right, it won’t look right, and it might even offend.
Effective translation and localization not only enhance customer experience but also drive loyalty and repeat business.
If you localize your store, you can expect to see an increase in organic traffic, conversion rates, a lower cart abandonment rate, and ultimately – accelerated growth.
So instead of asking ‘why do I need to launch a multilingual ecommerce store’, you should think more along the lines of ‘how can I fit localization into my strategy’.
Where do I start?
Before you even begin to localize your content, the first thing you need to consider is who’s your target market. So you’ll need to start with some research and prep work.
Choose your target market
Knowing who and where your target audience is helps you prioritize markets. So, first, you’ll need to understand if there’s product-market fit. You might already have noticed an increasing number of non-native speakers buying your products, which is a good sign that your product could benefit from localization.
But you’ll also need to consider market preferences. In some countries, shoppers might prefer a product that is not localized.
Tatiana Ryabinina, Co-founder & Localization Management Consultant at Grow-thru found that customers in Norway might prefer a product that is not localized because they were often exposed to poorly localized software. So they would expect localized products to be inferior and think that they are better off using the English version since they can.
She found the situation to be quite different in Mexico, where most customers didn’t understand English and would expect a fully localized experience.
The key is to choose strategically rather than spreading resources too thin. That could mean you start with the market that’s easiest to localize for, where cultural landscapes aren’t too different.
A good question to ask yourself is: What’s the extent of ecommerce localization that would be enough for [add your target market here] to buy my product?
For a more in-depth guide to choosing your target market, watch this webinar.
Choose your tech stack
Already have an ecommerce platform? If yes, the next step is to understand the level of localization you need to carry out.
If you have a small volume of content to translate and are not localizing to the full extent, you might be ok with copying and pasting translations from a translation tool,
But if you need to translate huge volumes of content and adapt content for different audiences, you’re better off using a translation management tool.
A translation management tool has built-in collaborative features that help retail companies quickly deliver local languages across thousands of product lines, while improving accuracy and ironing out the process.
If you don’t have an ecommerce platform and you know you want to localize either now or in the future, choose a platform that supports localization, such as Shopify or WooCommerce. These eCommerce platforms have integrations with translation management tools, so all you have to do is click and connect. You can also connect these eCommerce platforms to translation management tools through an API.
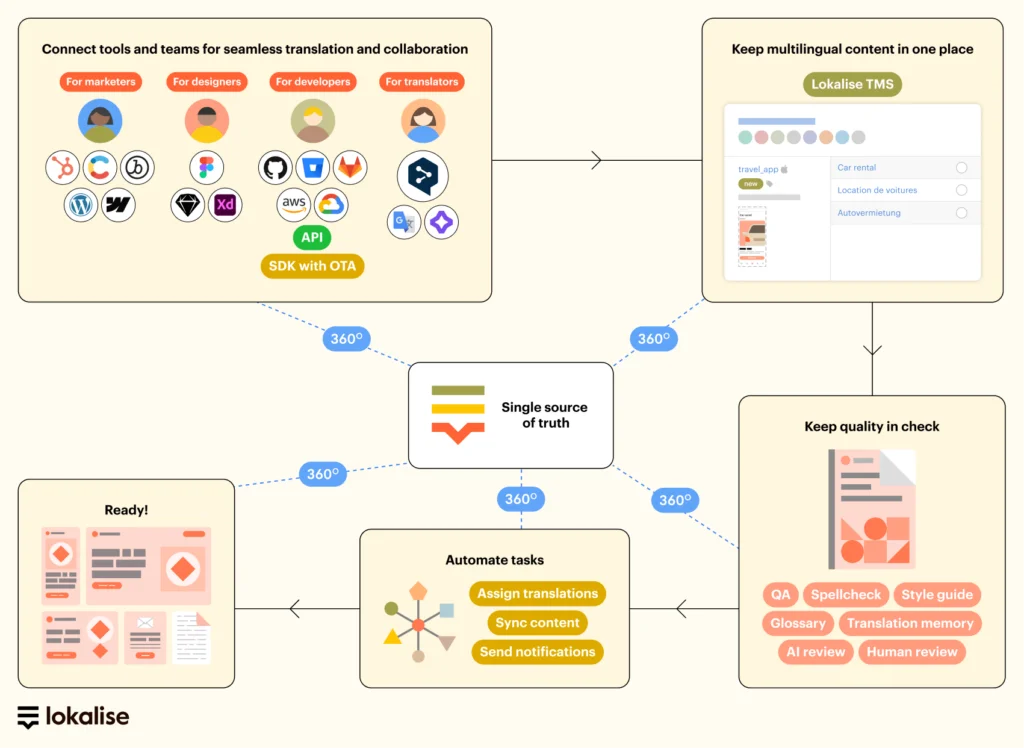
Once you’ve set up your ecommerce and localization tools, you’ll be able to:
- Manage translation and localization more efficiently
- Automatically synchronize source files across all languages whenever there’s an update
- Automate tasks and hand-offs, and reduce manual work
- Track changes and tasks, and avoid double work
- Increase speed to market
- Improve translation quality
- Get an overview of all your content in one place and avoid duplicates
- Make it easy for content writers, translators, designers, and developers to work together
- Speed up the development cycle with continuous localization
To help you choose the right TMS for your localization project, get this free TMS evaluation worksheet.
Build automated ecommerce localization workflows
In the fast-paced and ever-changing world of ecommerce, every second can impact your bottom line.
Think of the hundreds of seasonal offers you need to get out the door on time to 5+ countries. One small pricing error could lead to enormous losses.
That’s why accuracy, not only speed, is key to conveying the right message at the right time. One way to speed up your workflow is through automations.
We recommend using tools that manage the whole translation process for you, helping you automate all of this:
- Translations: set up automatic machine translation to make the translation process faster
- Tasks: automatically assign, complete, and hand off translation and localization tasks
- Sync content: automatically import new content for translation and publish as soon as it’s ready
Leverage translation memory
This nifty tool is often overlooked, but translation memory can be a game-changer for quickly translating product lines.
Translation memory is a tool that’s well-known in the translation space. It’s often built into translation management systems or CAT tools to help speed up the translation process and keep costs down.
It works by saving past translations that have already been approved and using them to translate similar content in the future. It can save huge amounts of time. Also money.

Imagine all the words you don’t have to translate if you use translation memory. 💭
Decide on key ecommerce elements to localize
Now, onto the key elements of localization.
Language
Language is a given and is the first element that most ecommerce sites focus on. When we talk about language in this instance, we’re talking about the words buyers see on a page. Though language could also refer to design, functionality, colors, symbols, tone… and so much more. But we’ll touch upon these elements later on.
When you buy clothes or anything online, you want to be able to read the terms and conditions, the product and checkout information, and speak to customer support in the language that you feel more familiar with.
The same goes for your customers. By adapting your store to your buyer’s language, you’ll instantly make them feel at home. But you need to consider language variations between regions too.
For example, French has many different variations:
- French for France
- French for Belgium
- French for Switzerland, and so on
So you need to make sure the descriptions, specifications, and reviews of products speak directly to local tastes, slang, and terminologies, as well as being grammatically and linguistically correct. That way your content will resonate more with target audiences.
Domain
By selecting the right domain structure you can create a sense of locality for customers worldwide. While a .com domain is well-known and widely used, international shoppers tend to have more confidence in country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) like .co.uk, .fr, .de, etc.
When expanding internationally, consider these domain options:
- Country-code top-level domains (ccTLDs): ideal for targeting specific countries (e.g., .es for Spain), ccTLDs improve local SEO and user trust but require more management and resources.
- Subdomains: using subdomains (e.g., de.example.com) with global domains allows for geographical targeting but can add technical and SEO complexities.
- Subfolders: subfolders (e.g., example.com/es/) on a single domain are easier to manage and consolidate domain authority but may not be as effective for country-specific targeting.
- Combination of subdomains and subfolders — offers detailed regional targeting under one main domain, though it can be complex to manage and may pose SEO and navigation challenges.
The best structure depends on your business goals, target markets, and resources. ccTLDs are great for a strong local presence but come with higher costs. Subfolders or a mix of subdomains and subfolders could be more efficient for targeting multiple language groups within a larger region.
SEO
Global expansion requires a robust international SEO (iSEO) strategy to make sure your website is findable in various languages. This involves exploring region-specific keywords and phrases to increase visibility on local search engines, making it easier for customers to find your products.
If you have an ecommerce app, you’ll need to optimize for different regional app stores to increase visibility and downloads.
Key steps for international SEO:
- Conduct keyword research: dive deep into keyword research to uncover popular search terms in your target audience’s native language. Beyond direct translations, discover local phrases that might be more relevant, guiding your content optimization.
- Choose the right URL structure: options like country-code top-level domains (ccTLDs), subdomains, or subdirectories can impact how easily users and search engines find and index your content.
- Localize content: adapt your content to match the cultural and linguistic context of your audience. This involves translating and culturally adapting your website content, including text, images, and multimedia elements.
- Implement hreflang tags: use hreflang tags to help search engines understand the language and region you want pages to target. This helps avoid duplicate content issues, which could affect your search rankings. Read about implementing hreflang tags below.
- Build local backlinks: start acquiring local backlinks to improve your site’s credibility and search rankings in different markets. Focus on creating quality content that attracts natural backlinks, and reach out about guest posting on relevant local platforms.
Understanding and implementing hreflang tags
Hreflang tags are HTML attributes that tell search engines the language and geographic target of a webpage. By using these tags, you make it easier for search engines to show the right page version to users based on their location and language. This is especially useful for online stores that target customers from different areas, as it helps avoid content duplication issues and makes search results more relevant.
To add hreflang tags to your site, there are three main methods, each suited for different needs:
- Directly in the HTML head section: This straightforward approach involves placing hreflang tags in the head of your webpage’s HTML code. For example, if your site is available in English, French, and Japanese, you would include links like these in your HTML:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://example.com/en/"> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="fr" href="https://example.com/fr/"> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="ja" href="https://example.com/ja/">
- In the HTTP Response header: This method is ideal for non-HTML documents, like PDFs. By adding hreflang tags to the HTTP headers, search engines can be directed to the correct language version of such content:
https://example.com/whitepaper.pdf>; rel="alternate"; hreflang="en", https://example.com/de/whitepaper.pdf>; rel="alternate"; hreflang="de",
- Through the sitemap: For sites with many pages, managing hreflang tags in your XML sitemap is more practical.
<url> <loc>https://example.com/blog/sample-article</loc> <xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://example.com/blog/sample-article"/> <xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="de" href="https://example.com/de/blog/sample-article"/> </url>
The best method for your site depends on its size and the nature of its content. Small sites may find it easier to add hreflang tags directly in the HTML of each page. Larger sites might benefit from using XML sitemaps for better management, while HTTP headers work best for non-HTML files like PDFs or media.
Using hreflang tags does more than just define the language of a page; it also links different language or regional versions of a page together. This connection helps search engines understand how these pages relate to each other, allowing them to share ranking signals. If one version of a page performs well, other versions could also see improved rankings.
Images
Adjusting imagery to reflect local customs, climates, and values, helps make your brand and products more appealing to your target market.
Showing climate-appropriate apparel at the right time of year, for example, lets potential buyers visualize products in their context, creating a stronger sense of identity. Remember, seasons are reversed in the Northern and Southern hemispheres!
AI tools can be used to recommend visuals that best engage audiences in different locales, even adjusting for local style preferences. A/B testing can help you refine visuals by identifying which images are more effective in making customers continue to purchase.
Pricing and currencies
Showing prices in local currencies is a no-brainer. Correct pricing and currency conversion simplify purchasing decisions and help avoid unexpected fees. It’s a critical element if you want to improve the shopping experience and avoid currency conversion confusion, as well as cart abandonment.
Remember to include local taxes and shipping costs in displayed prices, to give shoppers transparency. This will give them the confidence to continue to the next step of their purchase.
You can always refine pricing strategies later on using analytics and A/B testing tools to see what price works best and where.
Promotions
When launching promotions in different markets, align them with local events, holidays, and traditions, as well as peak shopping times. Since public holidays and shopping trends vary globally, what’s effective in one country might not work elsewhere.
For example, targeting Presidents’ Day for promotions makes sense in the US but wouldn’t resonate elsewhere.
To tailor your promotions effectively across different markets, consider using:
- Market research tools: to understand key shopping periods and holiday traditions in target regions
- Localization services: adapt your marketing content to match local languages and cultural norms.
- Social media analytics: understand insights on optimal posting times and product promotion strategies for regional audiences
- Email marketing platforms: segment audiences based on location so campaigns are more relevant to local events and holidays
Navigation
The way buyers navigate your site should feel intuitive. It should also meet their expectations, so you need to understand how international buyers interact with local ecommerce sites. Here’s how developers can leverage strategies and technical tools, including Figma, to enhance navigation:
- Understand cultural preferences: use analytics tools to understand how cultural differences impact user interactions with your site. This data helps identify areas where your navigation might not meet the needs of users from various regions.
- Use Figma for collaborative design: Figma is a key tool for designing responsive and localized navigation systems. Its collaborative features allow teams to work together in real-time, experimenting with different layouts and user flows. When connected to Lokalise you can even see how your website looks when displaying different language versions.
- A/B test: test various navigation structures to see what works best for different demographics. Figma can aid in the initial design phase of these tests, allowing for rapid prototyping of navigation variations.
- Responsive design with frameworks: frameworks such as Bootstrap or Foundation help ensure your navigation is responsive. Design your responsive menus in Figma first to see how they adapt across devices, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Integrate SEO and localization: optimize your site structure for local search engines to make sure navigation terms are relevant and search-friendly in each target market. Again, Figma can help visualize how these terms fit into your design aesthetically and functionally.
- Enhance accessibility: improve site accessibility, including keyboard navigation, by applying ARIA roles and landmarks. Use Figma to plan how these elements are integrated into your design, ensuring that all users can navigate your site efficiently.
- Use analytics for continuous improvement: tools like Google Analytics and Hotjar provide insights into user interactions, guiding further navigation optimizations. Figma’s iterative design process is perfect for quickly implementing changes based on these insights.
Payment methods
Tailoring payment options to local preferences is as important as pricing if you want to reduce checkout abandonment and improve the customer experience. Payment methods vary widely from one country to the next.
Take a look at the difference between payment preferences in France and China, for example:
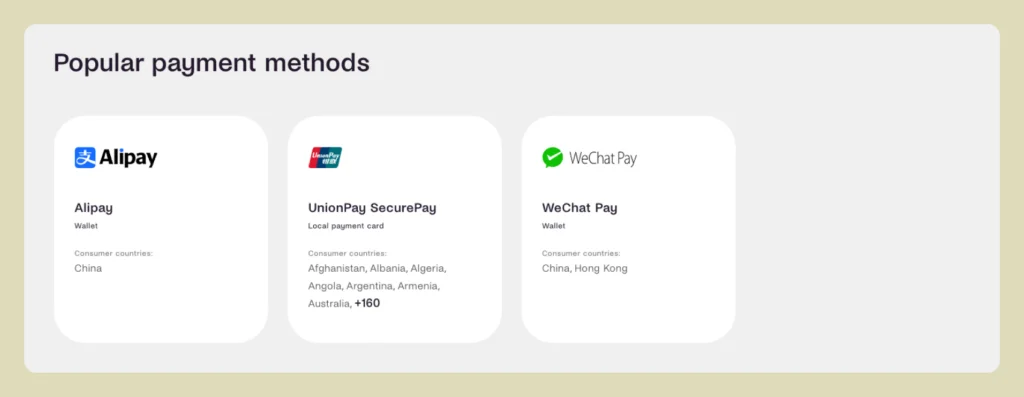

You can powerful platforms like Shopify Markets and robust payment gateways like PayPal, Stripe, and Adyen, which can accommodate a wide range of payment preferences, from digital wallets like Shop Pay and Apple Pay, to country-specific options like WeChat Pay in China and Klarna in Sweden.
You’ll need to use the APIs and SDKs that come with gateways, giving you the technical flexibility to implement various payment options seamlessly, ensuring a smooth checkout process.
You’ll also need to prioritize security in the integration process, implementing secure payment protocols while ensuring the payment interface is intuitive and localized.
In summary, a localized approach to payment methods in ecommerce involves:
- Choosing adaptable payment gateways (PayPal, Stripe, Adyen) that support global and local payment methods
- Utilizing APIs and SDKs for seamless integration of diverse payment options
- Ensuring security protocols and an intuitive user interface for a better checkout experience
- Tailoring payment options to match regional preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
Dates and times
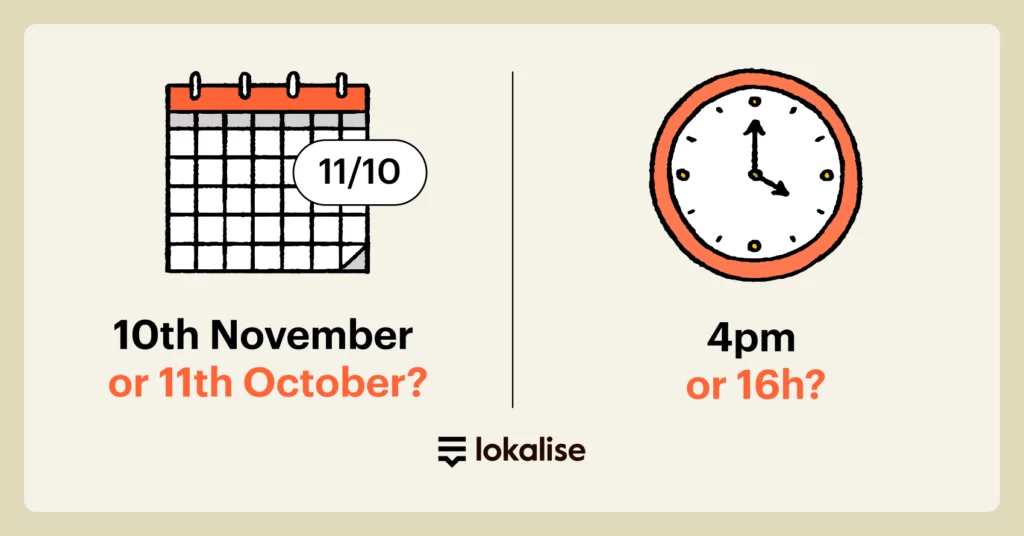
Regardless of a customer’s location, they should understand any time-sensitive information presented on your platform. Here’s how developers can tackle this challenge with the right tools and practices:
- Understand local norms: the first step in localizing dates and times is to understand the format used in your target markets. It can vary significantly between regions, such as the day-month-year format in many European countries versus the month-day-year format used in the US and Canada. Similarly, time formats can differ, with some countries using a 24-hour clock and others a 12-hour clock with AM/PM indicators.
- Use internationalization libraries: to manage these variations effectively, developers should leverage internationalization libraries. Libraries like Luxon and date-fns offer functionalities to format dates and times based on the user’s locale automatically. These libraries can detect the user’s location and apply the appropriate formatting rules, simplifying the localization process.
- Add locale detection: adding locale detection to your ecommerce app means local date and time formats will display automatically based on the user’s browser settings or account preferences. Tools such as i18next or JavaScript’s native Intl object allow for easy detection and application of locale-specific formats.
- Testing across locales: use browser developer tools to simulate various locales and check that your app correctly displays date and time formats across different locales. This step will help you catch any potential issues before they affect your users.
- Continuous localization: given the dynamic nature of global ecommerce, continuously updating and refining your localization efforts is important. Stay on top of changes in regional conventions or the addition of new markets to your ecommerce platform. Regularly review and update your localization libraries and custom implementations to maintain accuracy and relevance.
What your ecommerce localization workflow should and shouldn’t look like
Right, so, a lot of information. Phew. Don’t worry, here’s a quick recap of what your ecommerce localization process should and shouldn’t look like.
❌ How NOT to do ecommerce localization
Yey, you’ve got new content! But that means you’re going to have to go through the painstaking task of sharing it with translators, engaging in constant back-and-forths, providing context, and answering questions, while keeping track of everything and juggling tight deadlines.
And just when you think you’re done…
You get notified about a slight change in the source file and need to track and synchronize it across all languages you’ve already received translations for – all that manually.
Once you have the final copy, you realize there’s an unexpectedly long call-to-action in some languages which means designs need to be adjusted.
Finally, your developers can go ahead and publish.

Worried about the same process repeating with every single feature update?
✅ This is how to simplify ecommerce localization
- Connect your ecommerce platform, repositories, and CMS platforms to a localization management system via an API or integration. This allows the automatic transfer of new content and code changes into the localization workflow.
- Make collaboration easy. Support translators and reviewers with context-rich file formats like XLIFF or JSON and help marketing teams keep on top of content to adapt for different audiences.
- Use translation memory technology to repurpose previously translated content, reducing localization costs.
- Create automations to reduce manual tasks, like assigning translations and content syncs
- Facilitate collaboration with integrated commenting tools.
- Stay on brand with built-in style guides, glossaries, and stored translations.
- Easily weave in continuous localization workflows to keep up with ever-changing product lines
ecommerce localization success stories
Specialized: easy collaboration for translators, developers, and other teams
Specialized, a US-based global cycling brand turned to Lokalise for a streamlined localization process. The result? A unified platform that not only decreased the number of tools needed but also sped up turnaround times.
Tyler Brown, Software Development Manager at Specialized, shared, “Teammates finally have one place to go when updating or modifying translations across multiple products.”
Key results:
– Reduced tools required from many to just one (Lokalise)
– Faster turnaround with API automation
– Easy collaboration for translators, developers, and other teams
– Bulk project updates instead of manual editing
Zalando: customer-centric localization
The team at Zalando aim to be “really, really local” in their approach to localizing content for their 51 million active customers.
But they also try to be inclusive and break down barriers between countries that speak the same language by offering a more universal language.
Meggie Bouchard Bergevin, Product Leader at Zalando explains:
“There’s a language that is tied to the market that is based on the official way to speak French in France and the official way to speak French in Switzerland.”
“But then there is a universal French that wouldn’t be tied to any market and that would then be available.”
“So we’re in that space right now where things are looking like we’re trying to find ways to offer the user their preferred language and to kind of cut the barriers of countries and to be a little bit more inclusive in that way.”
Zalando has 7000 brands on its books but they’re not available in every market. So the team has content they localize based on where the marketing campaign is going live, as well as global marketing campaigns and regional marketing campaigns.
Meggie says: We are local, we are close to the customers and we tend to distribute local products as much as we can. And that shows in the languages that we use. But then we want to be global enough in the architecture.
That’s why Zalando has global URLs that are GEO-located based on where you are, when you browse marketing campaigns, for example.
They also focus on user personas and adapt content with transcreation tools. And that means they can propose a version of the content for specific users. Overall they try to make content feel as attuned to the customer as possible.
Final Thoughts
Ecommerce localization isn’t just a nice-to-have.
It’s a must for businesses looking to connect with a global audience.
By understanding your market, choosing the right tools, and setting up efficient localization workflows, you can make it effortless to open up shop in new markets.
Tune into our webinar, in partnership with Hygraph: Mastering the art of ecommerce without borders.
You’ll learn firsthand about ecommerce localization from industry experts who’ve worked at Nike and Siemens.